Understanding your devices’ technical specifications is crucial in today’s fast-paced digital world. One of the most common terms you’ll encounter is CPU speed, often measured in gigahertz (GHz).
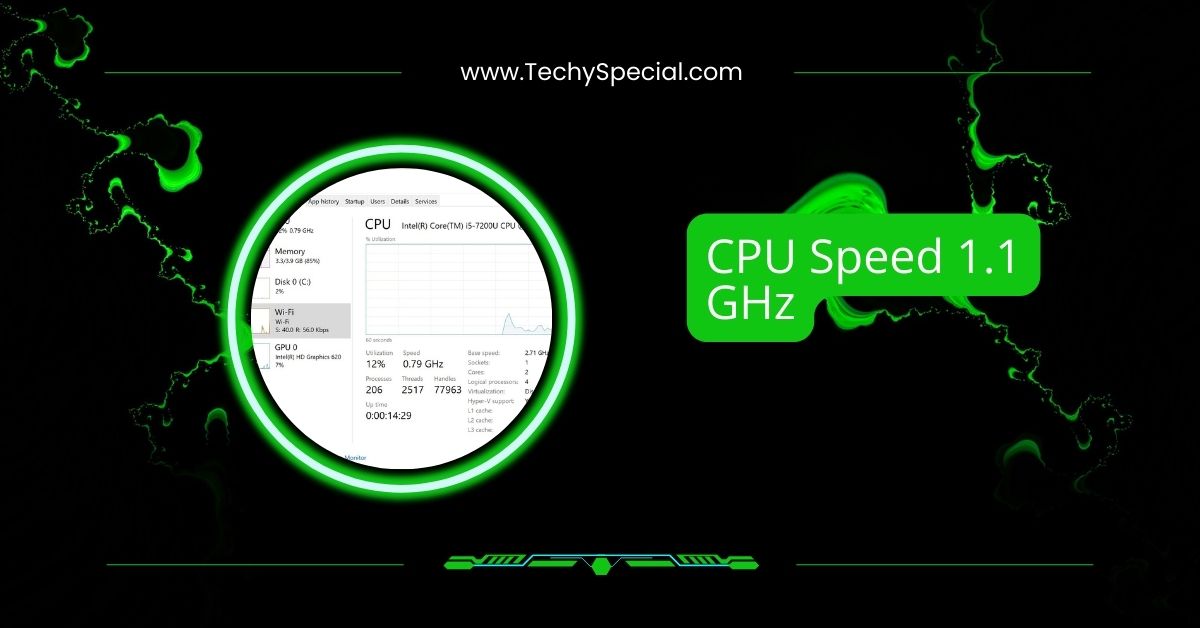
A 1.1 GHz CPU is a processor with a base speed of 1.1 billion cycles per second. It’s good for basic tasks like browsing and light work but not for heavy gaming or video editing applications.
This article will explain everything you need to know about CPU speed, specifically focusing on 1.1 GHz processors, and help you determine whether they’re the right choice for your needs.
What is CPU Speed?
The central processing unit (CPU), often referred to as a computer’s ” brain,” is responsible for executing instructions and performing calculations.
CPU speed, measured in gigahertz (GHz), indicates how many cycles a CPU can complete per second. For example, a 1.1 GHz CPU can complete 1.1 billion cycles per second.
However, CPU speed is just one factor that determines overall performance. Other factors, such as the number of cores, cache size, and architecture, also play a significant role.
What Does 1.1 GHz Mean?
A 1.1 GHz CPU is a processor with a clock speed of 1.1 billion cycles per second. While this may seem low compared to modern processors that often exceed 3 GHz, it’s essential to understand that clock speed alone doesn’t tell the whole story.
- Low Power Consumption: A 1.1 GHz CPU typically consumes less power, making it ideal for devices prioritizing battery life over raw performance.
- Entry-Level Performance: These processors are often found in budget-friendly laptops, tablets, and smartphones for basic tasks like web browsing, document editing, and media playback.
How Does a 1.1 GHz CPU Perform?
The performance of a 1.1 GHz CPU depends on the tasks you’re performing. Here’s a breakdown:
1. Basic Tasks
- Web Browsing: A 1.1 GHz CPU can handle light web browsing and streaming without issues.
- Document Editing: Word processing, spreadsheets, and presentations run smoothly.
- Media Playback: Streaming videos and music works well, especially at lower resolutions.
2. Moderate Tasks
- Multitasking: Light multitasking (e.g., having a few browser tabs open while editing a document) is possible but may slow down the system.
- Light Gaming: Older or less demanding games may run, but don’t expect high frame rates or graphics quality.
3. Heavy Tasks
- Video Editing: Not recommended for video editing or rendering.
- Gaming: Modern, graphics-intensive games will struggle to run on a 1.1 GHz CPU.
Use Cases for a 1.1 GHz Processor
A 1.1 GHz CPU is best suited for specific use cases:
1. Budget Devices
- Found in affordable laptops, tablets, and Chromebooks.
- Ideal for students or casual users who need a device for basic tasks.
2. Portable Devices
- Commonly used in smartphones and lightweight laptops where battery life is a priority.
3. IoT Devices
- Used in smart home devices, wearables, and other IoT applications that don’t require high processing power.
Pros and Cons of a 1.1 GHz CPU
1. Pros
- Energy Efficiency: Consumes less power, extending battery life.
- Cost-Effective: Affordable for budget-conscious users.
- Compact Design: Often found in lightweight, portable devices.
2. Cons
- Limited Performance: Struggles with demanding tasks.
- Not Future-Proof: This may become outdated as software requirements increase.
- Slow Multitasking: Performance drops with multiple applications running.
Factors That Affect CPU Performance
1. Clock Speed (GHz)
- Definition: Clock speed refers to the number of cycles a CPU can complete per second, measured in gigahertz (GHz). For example, a 1.1 GHz CPU can complete 1.1 billion cycles per second.
- Impact: Higher clock speeds generally mean faster processing, but only when comparing CPUs within the same architecture and generation.
- Limitation: Clock speed alone doesn’t determine overall performance, as other factors like cores and cache size also play a role.
2. Number of Cores
- Definition: Cores are individual processing units within a CPU. Modern processors can have anywhere from 2 to 64 cores.
- Impact: More cores allow a CPU to handle multiple tasks simultaneously (multitasking). For example, a quad-core processor can run four functions simultaneously, while a single-core processor can only handle one.
- Use Case: Multithreaded applications (e.g., video editing, gaming) benefit significantly from multiple cores.
3. Threads (Hyper-Threading)
- Definition: Threads are virtual cores created by technologies like Intel’s Hyper-Threading or AMD’s Simultaneous Multithreading (SMT).
- Impact: Each core can handle multiple threads, improving multitasking and performance in applications optimized for parallel processing.
- Example: A 4-core CPU with Hyper-Threading can handle 8 threads, doubling its multitasking capability.
4. Cache Size
- Definition: The CPU cache is a small amount of high-speed memory on the processor. It stores frequently accessed data for quick retrieval.
- Impact: A larger cache reduces the CPU’s time waiting for data from the slower RAM, improving overall performance.
- Levels:
- L1 Cache: Fastest but smallest (measured in KB).
- L2 Cache: Larger than L1 but slower.
- L3 Cache: Largest and shared among all cores.
5. CPU Architecture
- Definition: Architecture refers to the design and technology used in the CPU. Newer architectures are more efficient and powerful.
- Impact: A newer architecture (e.g., Intel’s Alder Lake or AMD’s Zen 4) can outperform an older one, even at the same clock speed.
- Example: A 1.1 GHz CPU from 2023 will likely outperform a 1.1 GHz CPU from 2010 due to architectural improvements.
6. Thermal Design Power (TDP)
- Definition: TDP measures the maximum heat a CPU generates under load, expressed in watts (W).
- Impact: Lower TDP CPUs are more energy-efficient and generate less heat, making them ideal for laptops and portable devices. Higher TDP CPUs are more powerful but require better cooling solutions.
- Example: A 1.1 GHz CPU with a TDP of 5W is more power-efficient than one with a TDP of 15W.
Is a 1.1 GHz CPU Right for You?
Choosing a 1.1 GHz CPU depends on your needs:
1. Choose a 1.1 GHz CPU If:
- You need a device for basic tasks like web browsing, email, and document editing.
- Battery life is a priority.
- You’re on a tight budget.
2. Avoid a 1.1 GHz CPU If:
- You plan to use your device for gaming, video editing, or other demanding tasks.
- You need a future-proof device that can handle evolving software requirements.
CPU Speed 1.1 GHz Windows 11
A 1.1 GHz CPU meets the minimum requirement for Windows 11 but may feel slow. It’s better for light use; consider a faster processor or more RAM for smoother performance.
Is 1.1 GHz Good for Gaming?
No, a 1.1 GHz CPU is not good for gaming. Most games need faster processors (2.5 GHz or higher) and a dedicated GPU. It can only handle very old or lightweight games.
Is 1.1 GHz Processor Speed Good for School?
Yes, a 1.1 GHz processor is good for school if you’re doing basic tasks like writing, browsing, or watching videos. It’s affordable and energy-efficient, perfect for students on a budget.
1.10 GHz Processor Is Good?
A 1.10 GHz processor is good for browsing, streaming, and light office work. It’s not powerful enough for demanding tasks but works well for essential, everyday use.
Is 1.1 GHz Good for a Laptop?

A 1.1 GHz laptop is good for basic tasks like browsing, emails, and light work. It’s energy-efficient and affordable but unsuitable for heavy gaming or video editing tasks.
CPU Speed 1.1 GHz Laptop
A 1.1 GHz laptop is lightweight, affordable, and great for basic tasks like browsing, emails, and document editing. It’s not suitable for heavy multitasking or demanding software but works for simple use.
Is 1.1 GHz Good for Programming?
A 1.1 GHz CPU is unsuitable for programming, especially for complex tasks or running multiple tools. It can handle basic coding but struggles with advanced programming. Consider a faster processor for coding.
1.1 GHz quad-core too slow?
A 1.1 GHz quad-core CPU is slow for heavy gaming or video editing but works for essential functions like browsing or office work. More cores help with multitasking, but higher clock speeds improve performance.
Intel Celeron 1.1 GHz vs 2.4 GHz
A 2.4 GHz Intel Celeron is faster than a 1.1 GHz one, making it better for multitasking and slightly demanding tasks. The 1.1 GHz version is more energy-efficient but slower, suitable only for essential use.
Is Quad Core 1.1GHz, up to 2.4GHz CPU ok?
Yes, a quad-core 1.1 GHz CPU that boosts up to 2.4 GHz is decent for light tasks and multitasking. The boost speed helps with short bursts of performance, making it suitable for everyday use.
Maximum speed is 1.1GHz but runns at 2.5GHZ???
This likely means the CPU has a base speed of 1.1 GHz but can boost up to 2.5 GHz when needed. It’s designed to save power at 1.1 GHz and perform faster during demanding tasks.
Will my laptop of 8GB RAM work fast with a processor of 1.10GHz?
An 8GB RAM laptop with a 1.10 GHz CPU will work fine for basic browsing or document editing tasks. However, due to the low clock speed, it may feel slow for heavy multitasking or demanding software.
Is an HP computer processor 1.10GHz strong enough to run a 2.0GHz program?
A 1.10 GHz HP processor can run a program requiring 2.0 GHz if the program involves peak performance. However, it may run slower or struggle if the program needs constant high-speed processing.
FAQs
1. What Does CPU 1.10 GHz Mean?
A 1.10 GHz CPU completes 1.1 billion cycles per second. It’s good for basic tasks like browsing and light work but not for heavy applications.
2. What is a Good CPU GHz Speed?
A good CPU speed depends on your needs. For basic tasks, 1.5–2.5 GHz works. For gaming or editing, aim for 3.0 GHz or higher.
3. How Powerful is a 1 GHz Processor? Is it Worth Buying One? If Not, What Processor Should I Buy?
A 1 GHz processor is weak for modern tasks. Avoid it for gaming or editing. Choose at least a 2.0 GHz processor for better performance.
4. The Laptop I Want Says It Has 1.1GHz of Processor but with a Burst Speed of 2.6GHz. What Exactly Does That Mean?
It means the CPU runs at 1.1 GHz for basic tasks but can boost up to 2.6 GHz for short bursts of high performance when needed.
5. Is a 1.1 GHz Processor Good? I Want to Get a New Laptop, and Everything Looks Good, but I Am Not Sure About the Processor.
A 1.1 GHz processor is good for browsing or office work. Choose a faster processor for gaming or heavy apps.
Conclusion
A 1.1 GHz CPU is ideal for browsing, document editing, and light multitasking. It’s energy-efficient and budget-friendly but struggles with demanding gaming or video editing applications. Consider a faster processor with higher clock speeds and more cores for heavy tasks.