Optimizing CPU VDD SoC current is a smart way to improve your processor’s performance, stability, and energy efficiency.
CPU Vdd SoC Current Optimization improves power efficiency, reduces heat, and enhances CPU performance by fine-tuning voltage settings. Proper optimization ensures stability, lower power consumption, and longer hardware lifespan, making your system run smoother and more efficiently.
In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about CPU VDD SoC current optimization in simple, easy-to-understand terms. Let’s get started!
What is CPU VDD SOC Current Optimization?
CPU VDD SOC current optimization adjusts voltage to the system-on-chip (SoC) for better efficiency and stability.
It helps reduce heat, improve performance, and extend hardware lifespan by fine-tuning power delivery based on workload needs, preventing unnecessary energy waste.
Understanding CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization refers to managing the electrical current supplied to a CPU’s system-on-chip (SoC).
By optimizing this current, users can strike the ideal balance between performance and energy efficiency, reducing power wastage and heat generation.
1. Understanding CPU Vdd Soc Current
CPU Vdd Soc current refers to the electric current flowing to the CPU’s System-on-Chip (SoC). This current powers the CPU and allows it to process tasks smoothly.
However, if too much current is delivered, it can lead to overheating and wasted energy. If it’s too low, performance may drop, causing system instability.
The goal is to balance this current for steady, efficient performance. Factors like workload, CPU design, and power settings play a role. By adequately managing CPU Vdd Soc current, your processor can perform at its best without wasting power.
2. Importance of CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
Optimizing CPU Vdd Soc current is essential for better performance and energy efficiency. It reduces power wastage, lowers heat output, and extends the lifespan of your CPU. In mobile devices, it means longer battery life.
For PCs, it ensures smooth performance during heavy tasks like gaming or editing. Without proper optimization, your system may overheat or become unstable.
You can avoid these problems by fine-tuning the current and enjoying a faster, more reliable experience. It’s a simple yet powerful way to enhance your device’s performance.
3. Factors Affecting CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
Several factors influence how well you can optimize CPU Vdd Soc current. The CPU’s design and architecture determine its power needs. A high-performance CPU might require more current, while energy-efficient models need less.
The workload also matters; heavy tasks demand more power, while idle states require less. Advanced manufacturing processes allow for better power control, while BIOS settings and firmware updates can help fine-tune optimization.
Understanding these factors ensures you adjust the current effectively, making your CPU more efficient and responsive.
4. Techniques for CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
There are various techniques to optimize CPU Vdd Soc current. Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling (DVFS) adjusts power based on the workload, saving energy when the CPU is idle.
Power gating shuts off unused parts of the CPU to conserve power. Clock gating minimizes unnecessary energy use by stopping inactive circuits. Integrated Power Management Units (PMUs) help control power delivery more precisely.
Finally, voltage scaling experiments allow users to find the perfect balance between performance and energy savings. These techniques are easy to apply and can significantly improve efficiency.
Advanced Techniques in CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
1. Emerging Technologies in CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
Technology is rapidly evolving to make CPU Vdd Soc’s current optimization more innovative and effective. AI-powered power management allows CPUs to learn and adjust voltage for better efficiency.
On-chip voltage regulators (VRs) bring power control inside the CPU, making adjustments faster and reducing energy loss. Low-power semiconductor materials help CPUs use less electricity while maintaining performance.
Another innovation is energy-aware computing, where systems adjust power dynamically based on workload predictions. These new technologies are making CPUs faster, more incredible, and more energy-efficient, leading to better gaming, work, and everyday performance.
2. Emerging Trends in Power Delivery
Power delivery is becoming more advanced, ensuring CPUs get the right energy. Multi-phase voltage regulators are helping CPUs receive smoother and more stable power, reducing energy loss.
Integrated power delivery (IPD) moves power control closer to the processor for better efficiency. Wireless power transfer is being explored for some applications, reducing the need for traditional power connectors.
Additionally, AI-driven power management makes systems smarter by adjusting power based on real-time usage. These trends are making devices faster, more reliable, and energy-efficient, improving performance while reducing wasted power.
3. Future Perspectives in CPU Vdd Soc Current Optimization
The future of CPU Vdd Soc’s current optimization looks exciting. Quantum computing breakthroughs could lead to processors that require much less energy. Graphene-based chips may replace silicon, offering ultra-efficient power usage.
Self-adjusting AI algorithms will help CPUs optimize voltage without human input, ensuring maximum performance with minimal energy waste. Green computing will push for lower power consumption in all devices, making technology more environmentally friendly.
As CPUs become faster and more complex, more intelligent power optimization will be key to balancing performance, battery life, and sustainability in the next generation of computing.
When Should You Optimize CPU VDD SOC Current?
You should optimize CPU VDD SOC current when experiencing high temperatures, instability, or excessive power consumption.
It’s also useful for overclocking, maximizing laptop battery life, or ensuring stable gaming and multitasking performance while controlling system temperatures.
How Does CPU VDD SOC Current Optimization Work?
This process adjusts voltage levels for the CPU’s SoC to balance power efficiency and performance. It lowers power usage when idle and increases it under heavy workloads, ensuring stable operation, reducing heat, and preventing system crashes while optimizing energy efficiency.
What is “CPU VDD_SoC Current Optimization”
CPU VDD_SoC current optimization helps balance power and performance by adjusting voltage for the system-on-chip (SoC).
This reduces heat, improves efficiency, and extends the CPU’s lifespan. Proper tuning ensures stable operation, especially for gaming and heavy workloads, without wasting power or causing overheating issues.
CPU VDDCR_VDD and VDDCR_SOC
VDDCR_VDD powers the CPU cores, while VDDCR_SOC supplies voltage to the integrated memory controller and other SoC functions.
Keeping these voltages balanced ensures stable performance. Setting too high can cause overheating, but too low may lead to system crashes. Proper tuning improves efficiency and stability.
Ryzen 5600X Good SoC & VDDG Voltages?
For the Ryzen 5600X, a suitable SoC voltage is around 1.0V-1.1V, while VDDG (fabric voltage) should stay around 0.95V-1.05V. Higher values can cause instability, while lower values may reduce performance.
Keeping them within recommended limits ensures better memory overclocking and stable system performance for gaming and multitasking.
CPU Core/CPU SoC Voltage Difference
CPU core voltage powers the central processing units, while CPU SoC voltage handles memory controllers and other integrated functions.
The core voltage is usually higher, around 1.2V-1.4V, while the SoC voltage stays between 1.0V-1.1V. Keeping both optimized ensures stable performance, especially when overclocking or running demanding tasks.
For Those Who Had Been Running 1.35V SoC for Weeks
Running 1.35V SoC for long periods can be risky. High voltage generates more heat and can degrade the CPU over time.
If you’ve been using this setting, it’s best to lower it to around 1.0V-1.1V for safety. Proper cooling and monitoring can help avoid long-term damage.
You Don’t Need High Voltages on the 5800X3D
The Ryzen 7 5800X3D is voltage-sensitive. Unlike other Ryzen CPUs, it doesn’t benefit from high voltages. Keeping SoC voltage around 1.0V-1.05V is ideal.
Higher values won’t improve performance and may cause instability. The chip’s design focuses on efficiency, so lower voltages work best for stability and longevity.
[Official] AMD Ryzen DDR4 24/7 Memory Stability Thread
This thread helps users find the best settings for 24/7 stable memory performance on Ryzen CPUs. It discusses recommended voltages, timings, and configurations for DDR4 RAM.
Users share their experiences to improve system stability while overclocking memory, ensuring smooth performance without crashes or instability.
Explaining the AMD Ryzen “Power Reporting Deviation” -metric in HWiNFO
“Power Reporting Deviation” in HWiNFO shows how accurately the CPU reports power consumption. Some motherboards tweak power limits, making readings less accurate.
A deviation above 100% means the system uses more power than reported. This is useful for understanding performance tuning and ensuring safe overclocking.
Overclocking Ryzen 5600X with PBO + AutoOC + Curve Optimizer + CPU VDD Telemetry Offset
Overclocking the Ryzen 5600X using PBO (Precision Boost Overdrive), AutoOC (Automatic Overclocking), and the Curve Optimizer help boost performance.
A CPU VDD telemetry offset can fine-tune voltage for efficiency. This method improves speeds while maintaining stability, giving better gaming and multitasking performance with optimized power usage.
The Role of BIOS Settings in CPU VDD SOC Current Optimization
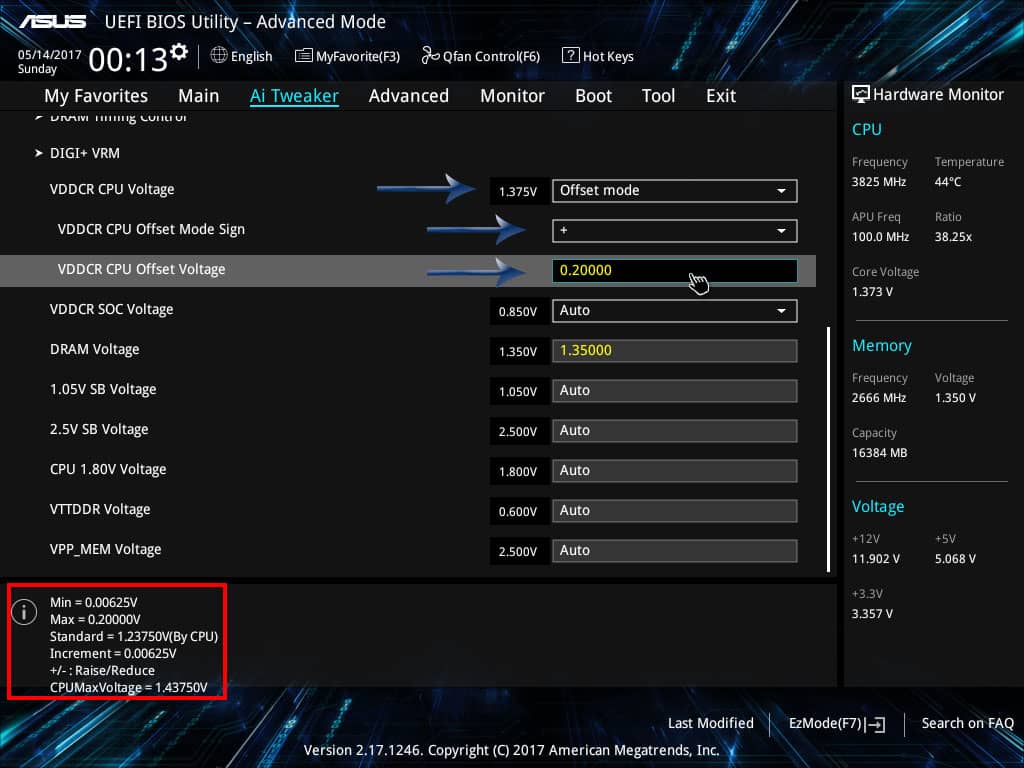
BIOS settings control voltage and power limits for the CPU’s SoC. Adjusting them can improve efficiency, stability, and performance.
Features like Dynamic Voltage Scaling (DVS) help balance power needs, ensuring lower heat output and longer hardware lifespan.
Benefits of CPU VDD SOC Current Optimization
- Better Performance – Ensures smooth and stable CPU operation without unnecessary power drain.
- Lower Power Consumption – Reduces energy use, making your system more efficient.
- Less Heat Generation – Helps keep temperatures lower, preventing overheating issues.
- Increased Hardware Lifespan – Reduces stress on components, leading to longer-lasting hardware.
- Improved Stability – Minimizes crashes, freezes, and unexpected shutdowns.
- Enhanced Battery Life – Optimizes power usage in laptops for extended battery performance.
- Optimized Overclocking – Helps achieve higher speeds while maintaining system reliability.
- Eco-Friendly Computing – Lowers electricity consumption, reducing environmental impact.
Common Issues Without CPU VDD SOC Optimization
- High Power Consumption – The CPU may use more power than needed, increasing electricity costs.
- Excessive Heat – Inefficient voltage settings can cause overheating, leading to thermal throttling.
- System Instability – Unexpected crashes, freezes, or reboots may occur due to power fluctuations.
- Reduced Hardware Lifespan – Overvolt can stress components, causing faster wear and failure.
- Lower Performance – Poor power management can lead to inconsistent CPU speeds and lag.
- Inefficient Overclocking – Unoptimized settings can limit stable overclocking potential.
- Shorter Battery Life – Laptops may drain batteries faster due to unnecessary power usage.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between CPU VDD and SOC VDD?
CPU VDD powers the processor cores, while SOC VDD supplies voltage to the system-on-chip components like memory controllers and integrated graphics.
2. What is CPU VDD full-scale current?
CPU VDD full-scale current is the maximum current the CPU can draw under peak load, ensuring stable power delivery for demanding tasks.
3. What does CPU VDD mean?
CPU VDD refers to the voltage supplied to the processor cores, controlling the CPU’s power consumption, performance, and stability.
4. What is CPU SOC voltage?
CPU SOC voltage powers the non-core components like memory controllers and integrated graphics, affecting stability and efficiency in modern processors.
5. What is CPU VDD SoC current optimization?
It fine-tunes power delivery to improve efficiency, reduce heat, enhance stability, and extend the lifespan of CPU and SoC components.
6. Is SoC the same as CPU?
No, the CPU handles processing, while the SoC integrates multiple components like CPU, GPU, and memory controllers for efficiency.
Conclusion
CPU Vdd SoC Current Optimization enhances performance, efficiency, and stability while reducing power consumption and heat. Proper tuning extends hardware lifespan, prevents crashes, and ensures smoother operation. Optimizing voltage settings helps achieve better system reliability, making your CPU run cooler and more efficiently.