CPU C-States are power-saving features designed to reduce energy use when your processor isn’t fully active.
Disabling CPU C-States can improve gaming performance by reducing input lag and stutters. However, it increases power consumption and heat. If you prioritize smooth gameplay, turning C-States off may help, but casual users can leave them enabled.
In this guide, we’ll break down what C-States do, their impact on performance, and whether turning them off is right for you.
Understanding CPU C-States
1. What Are CPU C-States?
CPU C-States are different power levels a processor can enter when it’s not working. Think of them like sleep modes on your phone.
The deeper the C-State, the less power the CPU uses. While this helps reduce heat and electricity use, switching back to full power can sometimes slow things down.
2. Types of CPU C-States
CPU C-States are divided into different levels, each offering varying power savings. Here are the main types:
- C0 (Active State): The CPU is fully powered and running at maximum performance.
- C1 (Halt State): The processor is idle but can quickly return to full speed.
- C2 (Stop Clock State): Some parts of the CPU are turned off to save power, but it can still wake up quickly.
- C3 (Sleep State): The CPU stops working, and cache memory is disabled. Waking up takes longer.
- C6 (Deep Sleep State): The CPU shuts down most of its functions, significantly reducing power use. It takes more time to wake up.
Higher C-States save more power but may cause small delays, so gamers often disable them for better performance.
3. How CPU C-States Work
When your computer is not busy, the CPU enters a lower power state to save energy. If it needs to process something, it “wakes up” and returns to full speed.
However, moving between states takes time, which can cause small delays. This is why some gamers disable C-States to ensure their CPU stays fully active all the time.
Benefits of CPU C-States
CPU C-States help manage power efficiently, reducing energy consumption and heat generation. While they may impact gaming performance slightly, they offer several advantages for most users.
1. Reduced Power Consumption
When the CPU is idle, C-States lower power usage by shutting down unused parts. This helps laptops last longer on battery and reduces electricity costs for desktop users.
2. Lower Heat Generation
Since the CPU uses less power in C-States, it generates less heat. This helps keep temperatures low, reducing the need for loud cooling fans and preventing overheating issues.
3. Improved CPU Longevity
Lower heat and power consumption mean less stress on the CPU, which can extend its lifespan. A cooler and more efficient processor is less likely to suffer from long-term wear and tear.
4. Environmental Benefits
CPU C-States help lower overall electricity use by reducing energy consumption, making computers more eco-friendly. This is especially beneficial for data centers and offices with multiple systems.
5. Quieter System Operation
Since C-States reduce heat, the CPU fan doesn’t have to work as hard, leading to quieter system performance. This is great for users who prefer a silent PC environment.
Disadvantages of CPU C-States for Gaming
While CPU C-States help save power and reduce heat, they can negatively impact gaming performance. Here are some key disadvantages for gamers.
1. Increased Latency
When the CPU enters a low-power state, it takes time to “wake up” and return to full speed. This delay can cause a slight lag in fast-paced games, affecting reaction times.
2. Reduced Performance Stability
Frequent switching between power states can cause small performance drops, leading to occasional stutters or frame rate inconsistencies during gameplay. This is especially noticeable in competitive gaming.
3. Potential Input Lag
Since the CPU takes longer to respond, it can create minor input delays. This means shooting or jumping in games might feel slightly less responsive.
4. Incompatibility with High-Performance Gaming
Some high-end gaming PCs and overclocked CPUs perform better with C-States disabled. Deep sleep modes can interfere with sustained high performance, making the system less reliable during intense gaming sessions.
5. Possible System Instability
Enabling deep C-States can cause crashes, freezes, or unexpected slowdowns in games in rare cases. This happens because the CPU takes longer to recover from a low-power state, affecting real-time performance.
CPU C-States and Gaming Performance
1. Impact on Gaming FPS
CPU C-States don’t directly reduce FPS but can cause minor stutters. Disabling them keeps the CPU active, ensuring smoother frame rates, essential for competitive and high-speed action games.
2. Input Lag Considerations
C-States can introduce slight input lag since the CPU takes time to “wake up.” Disabling them helps in fast-paced games where instant response times are crucial, like shooters and racing games.
Should You Turn Off CPU C-States for Gaming?
1. When to Disable C-States
If you’re a competitive gamer, experience stutters, or use an overclocked CPU, disabling C-States can improve performance. It ensures the CPU stays active, reducing latency and making gameplay smoother.
2. When to Leave C-States Enabled
For casual gaming, daily tasks, and power savings, leaving C-States on is better. It helps reduce heat, lowers electricity use, and extends CPU lifespan without significantly affecting gameplay.
How to Disable or Enable CPU C-States
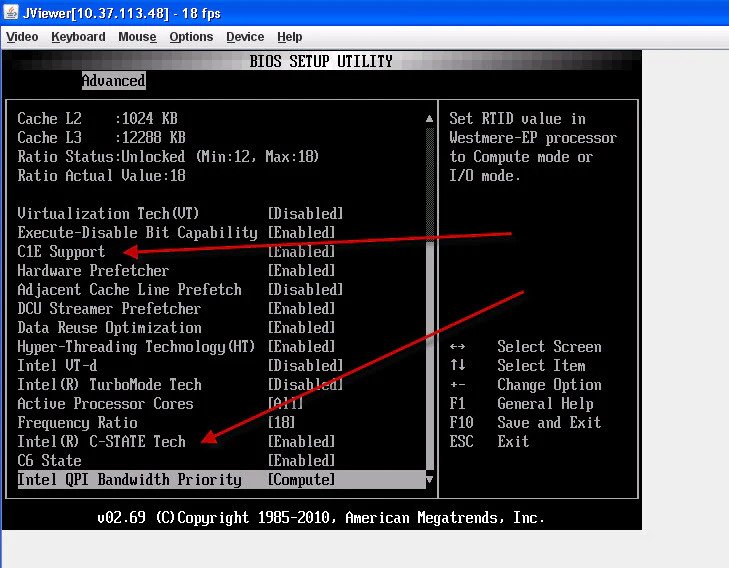
1. BIOS Settings Overview
You can adjust CPU C-States in the BIOS. To access it, restart your PC and press F2, Delete, or F12 (depending on your motherboard). Look for “Advanced CPU Settings” or “Power Management.” You can turn C-States on or off from there based on your needs.
2. Step-by-Step Guide
- Restart your PC and enter BIOS by pressing F2, Delete, or F12.
- Go to Advanced CPU Settings or Power Management.
- Find CPU C-States and toggle them On or Off.
- Save changes and exit BIOS.
- Restart your computer to apply the new settings.
Disable C-States AMD
On AMD processors, C-States can be disabled in the BIOS under Global C-State Control. This prevents the CPU from entering low-power modes, ensuring stable gaming and heavy task performance. It helps reduce lag but may increase power usage and heat.
Intel C-State On Or Off
Enabling C-States saves power and reduces heat for Intel CPUs, but it might cause small delays in gaming. Disabling them keeps the CPU fully active, improving responsiveness. Gamers often turn them off for better performance, while casual users leave them on for efficiency.
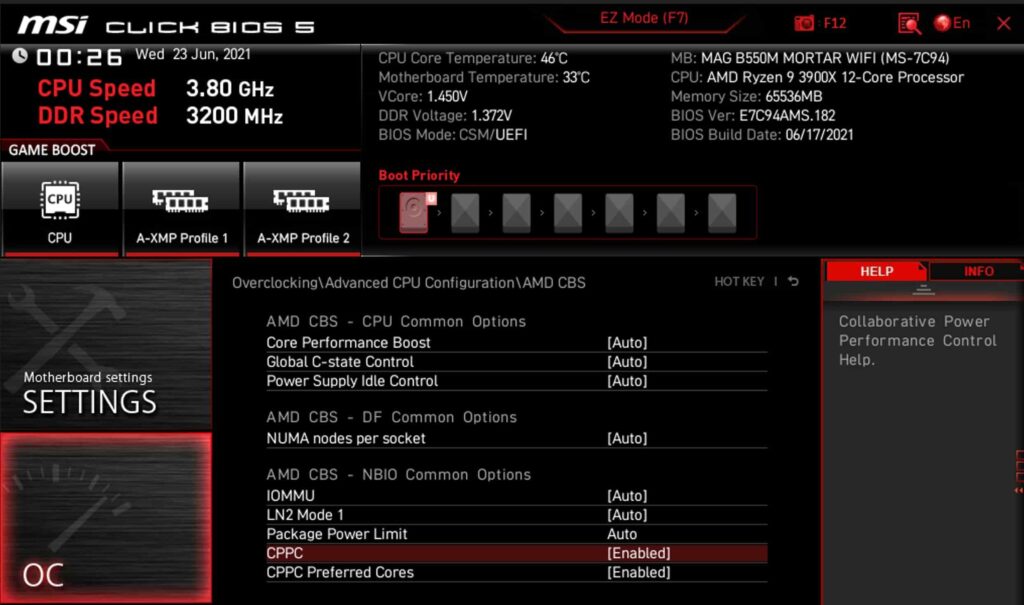
Global C-State Control
This setting in AMD BIOS manages power-saving modes. Turning it off forces the CPU to stay active, improving gaming performance.
Keeping it on reduces power usage and heat but might cause occasional stutters. Adjusting this depends on whether you prioritize speed or efficiency.
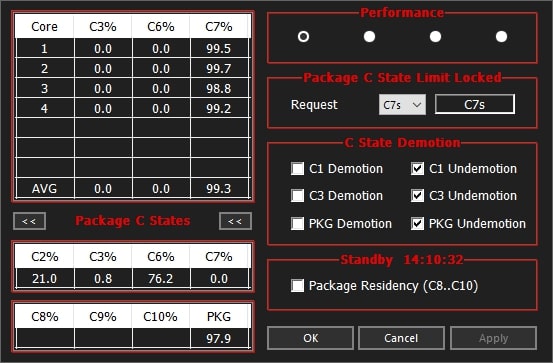
Package C-State Limit
This BIOS setting controls how deep the CPU can enter sleep modes. A lower limit means the CPU stays more active, improving performance. Setting it to C0 or C1 helps reduce lag in gaming, while higher values save power for regular tasks.
Disable C States Windows 11
You can disable C-States in Windows 11 through the Power Plan Settings. Set your plan to High Performance, disable CPU power-saving options, and adjust the Minimum Processor State to 100%. However, complete control requires changing settings in the BIOS.
Disable C States Gigabyte
On Gigabyte motherboards, enter the BIOS by pressing Delete at startup. Go to Advanced CPU Settings, find C-States, and disable them.
This keeps the CPU fully active, reducing latency in games but slightly increasing power consumption. Save changes before exiting.
CPU C State Capability?
CPU C-State capability refers to how well a processor can manage power-saving modes. Modern CPUs support deep C-States to reduce energy use.
However, disabling deeper states can improve gaming performance by keeping the processor awake and ready for immediate tasks.
CPU C States Enable Or Disable
Enable C-States for lower power usage, reduced heat, and improved efficiency in daily tasks. Disable them for better gaming performance, reduced stutter, and lower input lag. The best setting depends on whether you prioritize energy savings or smoother gameplay.
C-States On Vs Off. 100 Point Improvement
Turning C-States off can improve gaming responsiveness and reduce lag. Some users report up to a 100-point improvement in benchmark scores.
However, it increases power usage and heat, so the choice depends on whether you prioritize performance or efficiency.
Disable Intel C-State And Save Your Sanity
If you’re experiencing stutters, input lag, or freezes, disabling Intel C-States may help. It forces your CPU to stay active, reducing performance drops. However, it may cause higher temperatures and power consumption, so monitor your system accordingly.
Disabling C States Vs Limiting It To C0
Disabling C-States entirely prevents power-saving modes, keeping performance stable. Limiting it to C0 allows minimal power savings while maintaining high responsiveness. Setting it to C0 may work better than disabling it if you want the best balance.
Disabled CPU C-States And Sleep Mode
Disabling CPU C-States can sometimes prevent your computer from entering sleep mode correctly. Since the CPU stays fully active, sleep mode may become unreliable or stop working. Consider this before making permanent changes in the BIOS.
Do You Have Intel C State Disabled Or Enabled?
Check your BIOS under Advanced Power Settings to see if C-States are enabled or disabled. Disabling them might help if you experience lag or stutters while gaming. However, if your system runs cool and stable, leaving them enabled is fine.
Disabled C-State Impact On Electric Bill?
Disabling C-States makes the CPU use more power, slightly increasing your electricity bill. While the difference is negligible for personal computers, it can add up for multiple systems, like in data centers or offices. Expect a bit more heat, too.
Intel C-States Off – Better Ssd Performance!
Disabling C-States can improve SSD performance by reducing power state transitions that slow down data transfers.
Keeping the CPU awake helps maintain fast response times, smoothing SSD operations, especially in demanding tasks like gaming or video editing.
Should I Leave Global C-States Disabled By Default?
For general use, leaving Global C-State Control enabled is fine. It helps save power and reduce heat. However, if you experience stuttering in games or use an overclocked system, disabling it may improve overall performance and responsiveness.
Should I Disable CPU C States With An Intel Non K CPU?
If you have a Non-K Intel CPU (non-overclockable), disabling C-States may not provide a huge performance boost.
However, if you experience stutters, it might help. If everything runs smoothly, there’s no strong reason to turn them off.
Turn Off C-States When Gaming/Ocing And Turn On When Idle
An innovative approach is to disable C-States while gaming or overclocking for stability and lower latency. When not gaming, re-enable them for power savings and lower heat. This method offers the best mix of performance and efficiency.
Disabling C-States Fixed Freezes… Now What?
If disabling C-States fixed freezing issues, your CPU likely struggled with power transitions. Keep monitoring temperatures and stability.
If power usage isn’t a concern, leave them off. Otherwise, try limiting them to C0 or C1 instead of complete disablement.
No C-States = Lower Performance, C-States = Unstable, Help
If disabling C-States lowered performance, your CPU might rely on power management features. If enabling them causes instability, try updating your BIOS or adjusting power settings instead of disabling them. Finding a balance is key for smooth performance.
FAQs
1. What are CPU C States and why are they important?
CPU C-States are power-saving modes that reduce energy use when idle. They help lower heat and power consumption but can slightly affect gaming performance.
2. How can I enable or disable CPU C States?
Enter your BIOS, navigate to Advanced CPU Settings, find C-States, and toggle them on or off according to your performance needs.
3. Should I enable or disable CPU C States for better performance?
Disable them for gaming and low latency. Enable them for general use and power efficiency to reduce heat and electricity consumption.
4. Can enabling or disabling CPU C States affect system stability?
Yes, enabling them can cause slight lag, while disabling them may increase power use and heat but improves performance in some cases.
5. Are CPU C States supported by all processors and operating systems?
Most modern CPUs and operating systems support C-States, but settings may vary depending on your hardware and BIOS version.
6. Should Global C-State be “Enabled” instead of “Auto” on AM5 X3D processors?
Auto is fine for best efficiency. However, enabling it manually can ensure that power-saving features work properly without unnecessary limitations.
7. Will there be any negative effects on my CPU and its lifespan if I disable Global C-States in my BIOS?
Disabling C-States slightly increases power consumption and heat, but it won’t harm your CPU as long as cooling is sufficient.
8. Why, when I disable C-States in BIOS, is the frequency of my processor limited to 4800MHz?
Disabling C-States can prevent proper power scaling, locking your CPU at a lower clock speed to maintain stability and avoid overheating.
Conclusion
CPU C-States help save power and reduce heat but can slightly affect gaming performance. Disabling them improves responsiveness but increases power usage. Gamers may benefit from turning them off, while casual users should keep them enabled for efficiency and longevity.