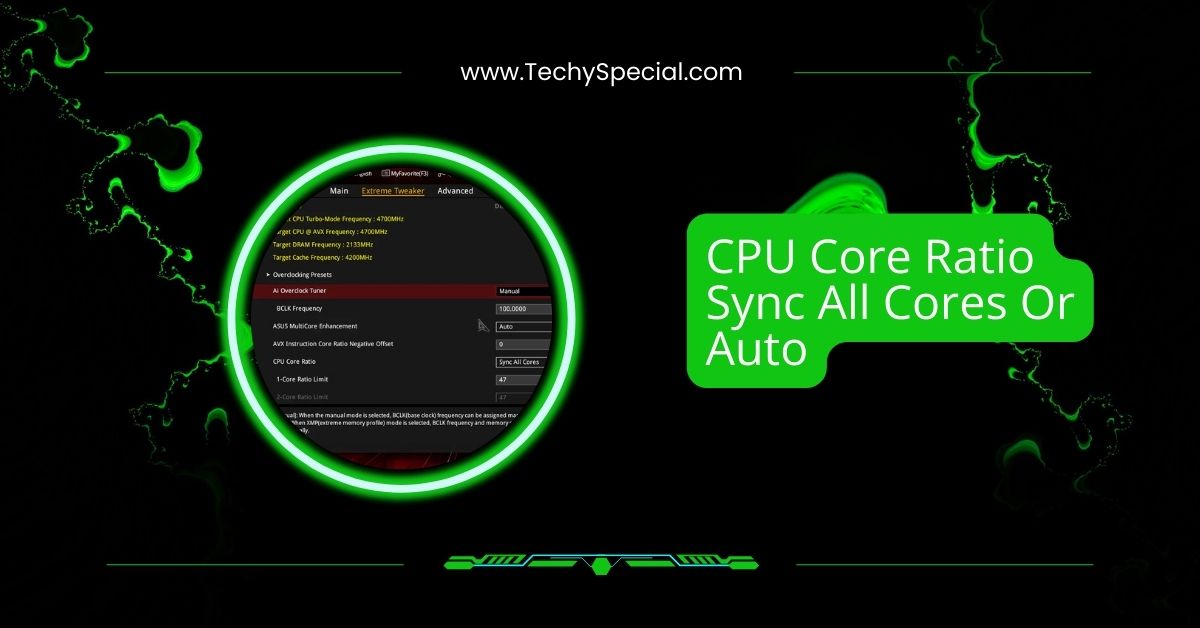
Choosing between Sync All Cores and Auto in your CPU settings can impact performance, power efficiency, and temperature.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto determines how your CPU cores operate. Sync All Cores sets the same speed for all cores, while Auto adjusts dynamically for efficiency and performance. Choose based on workload, power usage, and performance needs.
In this guide, we’ll break down the differences, benefits, and best use cases in simple terms so you can make the best choice for your needs!
Understanding CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores or Auto
The CPU Core Ratio Sync setting controls how your processor manages its speed. If you choose “Sync All Cores,” all CPU cores will run at the same speed, giving stable performance.
If you select “Auto,” the CPU will adjust the speed of each core based on the workload, balancing performance and power efficiency.
This setting is crucial because it affects your computer’s speed, temperature, and power usage. Choosing the right option depends on how you use your PC—whether for gaming, work, or everyday tasks.
1. The Difference Between All Cores and Auto
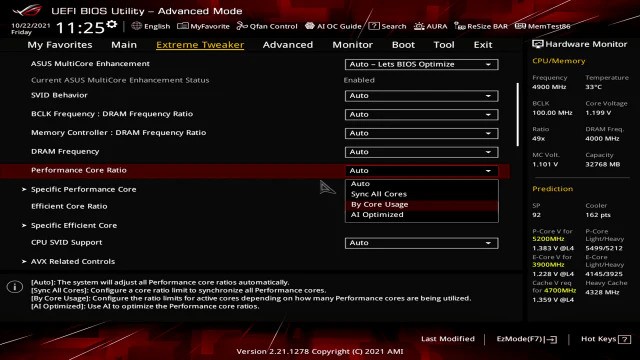
The All Cores mode runs every CPU core at the same speed, which is great for tasks requiring constant high performance, like video editing and 3D rendering. However, it also produces more heat and uses more power.
The Auto mode lets the CPU decide how fast each core should run based on your actions. This helps save energy and keeps your system cooler. Auto mode is better for general use and gaming, where performance changes depending on the game’s needs.
2. All Cores Mode – When and Why to Use
The All Cores mode is useful when you need maximum performance for demanding tasks. It’s great for:
- Video editing and 3D rendering require all CPU cores running at full speed.
- Overclocking – Sync All Cores ensures stable performance if you want more power.
- Heavy multitasking – Running multiple robust programs simultaneously benefits from a steady CPU speed.
However, this mode also increases heat and power usage, so you’ll need a sound cooling system to avoid overheating.
A. Steps to Enable All Cores Mode
- Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI by pressing the Del, F2, or F10 keys (varies by brand).
- Go to CPU Settings or Advanced Settings in the BIOS menu.
- Look for CPU Core Ratio Sync and choose “Sync All Cores.”
- Save the changes by pressing F10 and restart your PC.
- Once your system reboots, use Task Manager or monitoring software like HWMonitor to check if all cores are running at the same speed.
3. Auto Mode – When and Why to Use
Auto mode is perfect if you want your CPU to adjust its speed automatically based on what you’re doing. It works best for:
- Everyday tasks like web browsing and watching videos.
- Gaming, where the CPU needs to boost performance only when necessary.
- Keeping your PC cool by lowering power usage when full performance isn’t needed.
This mode is best for general users who want a balance between performance, energy savings, and temperature control without manually adjusting settings.
A. Steps to Enable Auto Mode
- Restart your PC and enter BIOS/UEFI by pressing Del, F2, or F10.
- Navigate to CPU Settings or Advanced Options.
- Locate CPU Core Ratio Sync and select “Auto.”
- Save the settings by pressing F10 and restart your PC.
- After rebooting, your CPU will automatically manage core speeds based on workload.
This mode is easy to use and ensures the best balance between performance and efficiency.
Fine-Tuning Performance with CPU Core Ratio Sync
CPU Core Ratio Sync lets you adjust how your CPU runs to match your needs. You can set all cores to the same speed if you need high performance.
If you want better efficiency, Auto mode lets the CPU adjust speeds based on workload. Some users manually tweak individual cores to balance speed and power savings.
This helps in gaming, video editing, or programming. However, making the wrong adjustments can cause overheating, so proper cooling is essential.
1. Overclocking Considerations
Overclocking boosts your CPU’s speed beyond its default limits, giving you faster performance in games and heavy tasks. “Sync All Cores” keeps all cores at the same speed, improving stability.
However, overclocking increases heat and power usage, so you’ll need a good cooling system to prevent overheating.
If not done correctly, it can cause system crashes or damage your CPU. Constantly monitor temperatures and adjust settings carefully to get the best performance without risks.
Optimizing Your CPU for Efficiency and Performance
You need the correct settings to get your CPU’s best performance and efficiency. If you do heavy tasks like gaming or video editing, “Sync All Cores” ensures all cores run at full speed.
“Auto” mode helps save power and reduce heat by adjusting core speeds as needed for everyday use. Keeping your CPU cool with a good fan or liquid cooling is essential. Also, updating drivers and using power-saving options can help maintain smooth performance.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Windows 11
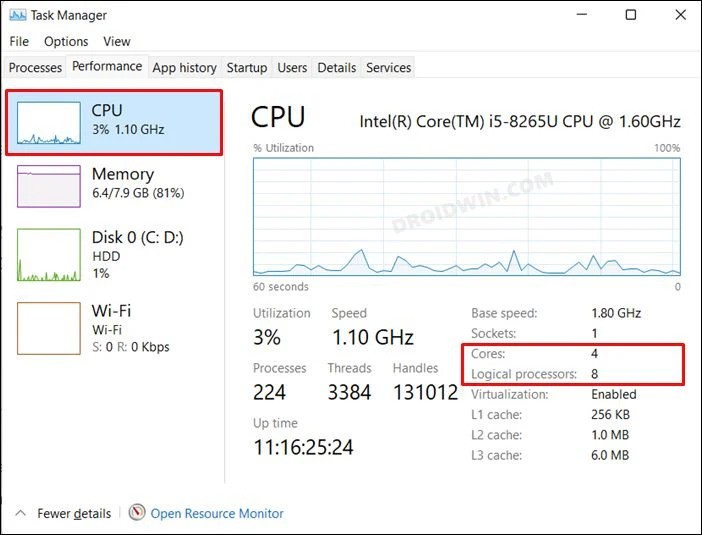
In Windows 11, you can set the CPU Core Ratio to “Sync All Cores” for better speed or “Auto” for balanced performance.
Syncing all cores helps with heavy tasks, while Auto mode saves power and reduces heat. Adjust this in the BIOS settings for better performance.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Windows 10
Windows 10 users can tweak the CPU Core Ratio in the BIOS to either Sync All Cores for stability or Auto for smart adjustments.
Syncing helps with intensive tasks, while Auto boosts efficiency. Choose based on your workload and cooling setup to keep your system running smoothly.
CPU Core Ratio Sync All Cores Or Auto Gaming
Sync All Cores can provide better FPS and stability for gaming, especially in CPU-heavy games. However, Auto mode lets your CPU manage power efficiently, avoiding overheating. If your game uses multiple cores, syncing them may help, but Auto works just fine for most games.
How To Sync All Cores
To sync all cores, enter your BIOS/UEFI settings, find CPU Core Ratio, and set it to “Sync All Cores”. Save and restart your PC.
This ensures all cores run at the same speed, improving performance in multi-threaded applications like video editing and rendering.
All Core Ratio Limit
The All Core Ratio Limit defines the maximum speed for all CPU cores. Setting it too high can cause overheating or system crashes, so ensure proper cooling. Keeping it within safe limits ensures stability and a long CPU lifespan, especially for overclocking.
13900k Sync All Cores
Syncing all cores on the Intel i9-13900K can boost performance, especially for demanding workloads. However, this processor already has dynamic frequency scaling, so Auto mode works well.
If overclocking, ensure proper cooling, as high power usage can lead to heat issues without adequate ventilation.
CPU Core Ratio AI Optimized
The AI Optimized option in BIOS automatically adjusts CPU core ratios for best performance and efficiency.
It uses machine learning to optimize speeds, making it great for those who don’t want manual tuning. This setting balances speed, power, and cooling based on your workload.
Is Sync All Cores the same as Limit Core Ratio?
No, Sync All Cores makes all cores run at the same speed, while Limit Core Ratio sets the maximum frequency they can reach.
Syncing boosts performance but increases heat, whereas limiting helps control power and temperature for stability.
8700K Sync All Cores vs Per Core Overclocking
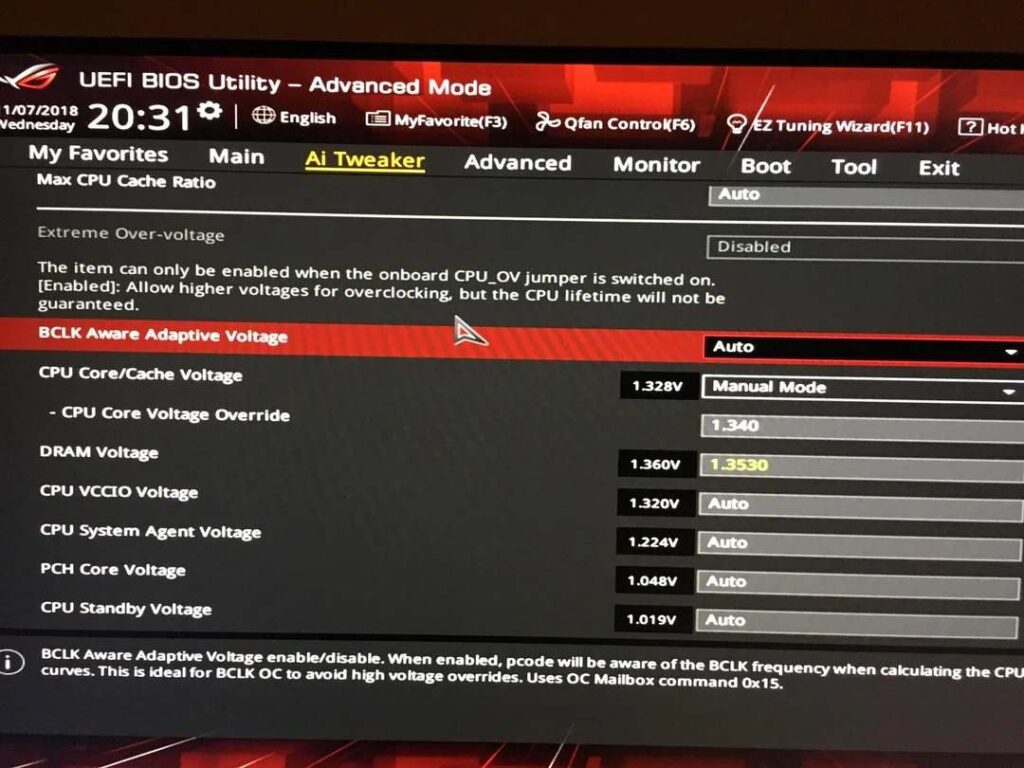
Syncing all cores on the i7-8700K ensures stable multi-core performance, while per-core overclocking allows higher single-core speeds.
Syncing works best for rendering and multitasking, whereas per-core tuning helps with gaming and lightly threaded applications needing higher boost clocks.
i9 13900K Sync All P Cores or Not?
For the i9-13900K, syncing all Performance (P) cores improves multi-threaded workloads but increases power usage and heat.
Letting Auto mode or per-core adjustments manage cores dynamically provides better efficiency, especially for gaming and single-core performance.
Per Core vs All Core When Overclocking?
All-core overclocking gives consistent speed across all cores, which is excellent for heavy multitasking. Per-core overclocking allows higher speeds on fewer cores, which is ideal for gaming. Choose based on your workload and cooling capabilities to avoid overheating.
Sync All Cores Asus ROG Strix Z590 WiFi
On the ROG Strix Z590, you can enable Sync All Cores in BIOS for stable multi-core performance. However, this can cause higher temperatures. If your cooling isn’t strong, consider Auto mode for a balance of speed and efficiency.
Is There Any Performance Gain from Syncing All CPU Cores?
Syncing all cores improves performance in multi-threaded applications like video editing and rendering. However, performance gains are minimal in gaming and daily use. It can also increase power consumption and heat, requiring better cooling solutions.
Is It Better to Sync All Cores and Should I Let My CPU Throttle Down?
Syncing all cores is excellent for performance but increases heat and power usage. Letting your CPU throttle down when idle saves energy and keeps temperatures low. It’s best to balance settings based on your needs and cooling.
How to Get All CPU Cores on One Clock Speed but Single Core on a Different One?
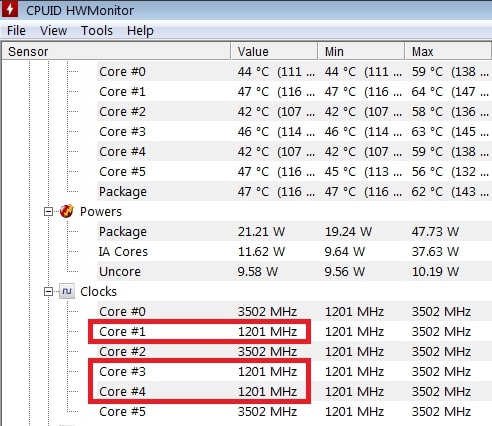
To do this, go into BIOS settings, set a fixed clock for all cores, and manually adjust per-core ratios. This allows high single-core boost speeds while keeping multi-core performance steady for tasks that need it.
Rendering + Gaming: Multicore Enhancement vs Sync All Cores vs Intel Specifications
For gaming, Intel stock settings work best. Sync All Cores helps in heavy workloads like rendering, while Multicore Enhancement (MCE) boosts performance at the cost of higher heat and power consumption. Choose based on task priority and cooling.
FAQs
1. Is it better to sync all cores or auto?
Auto is better for efficiency and lower temperatures while syncing all cores improves performance for heavy tasks like rendering and multitasking.
2. Should CPU core ratio be auto?
Yes, Auto mode balances performance and power efficiency, adjusting core speeds dynamically based on workload to prevent overheating and wasted energy.
3. Should I activate all cores on my CPU?
Auto works best for gaming and everyday use. Activate all cores for video editing, rendering, and heavy multitasking for maximum performance.
4. What is the best CPU ratio mode?
The best mode depends on usage. Auto for efficiency, Sync All Cores for powerful workloads, and Per Core for gaming optimization.
5. Does enabling all CPU cores increase performance?
Yes, for multi-threaded tasks like rendering and 3D modeling. Performance gains are minimal for gaming and light tasks, but power usage increases.
6. Does more cores reduce CPU usage?
Yes, more cores help spread the workload, reducing usage on individual cores. However, performance gains depend on software optimization and task type.
7. Does number of cores affect performance?
Yes, more cores improve multi-threaded performance. But higher clock speeds matter more than the core count for gaming and light tasks.
8. How do I make sure I use all CPU cores?
Enable Sync All Cores in BIOS, check Task Manager for usage, and optimize software settings to utilize multiple cores efficiently.
Conclusion
Choosing between Sync All Cores and Auto depends on your needs. Sync All Cores boosts performance for demanding tasks, while Auto optimizes power and temperature. For most users, Auto works best, but advanced users can tweak settings for maximum efficiency and speed.