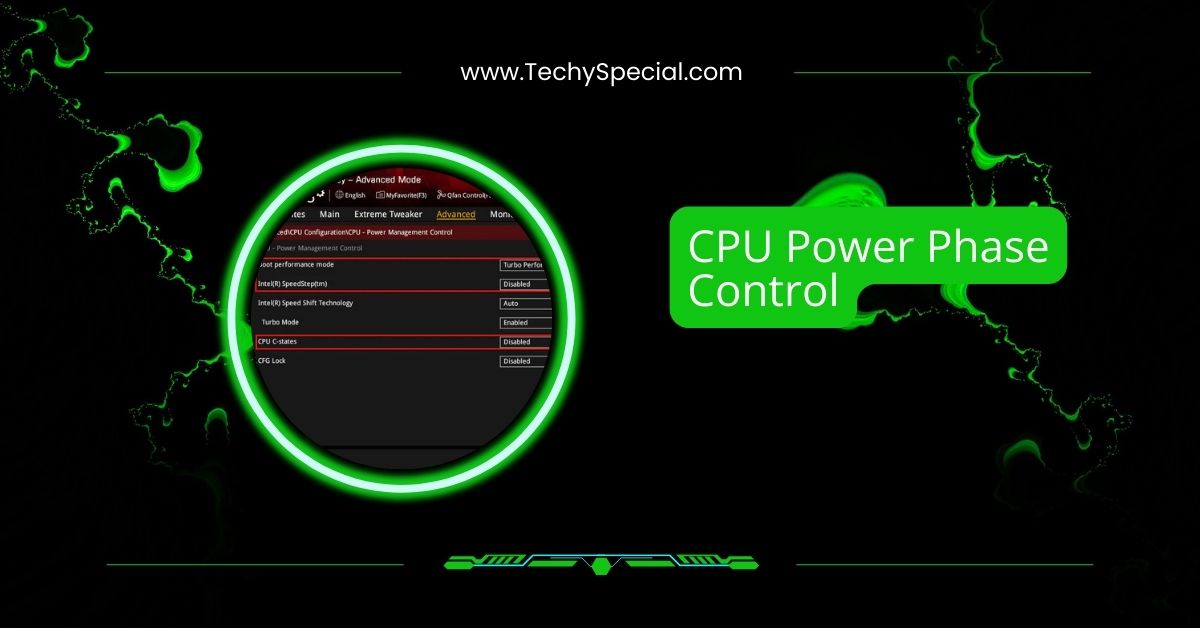
CPU Power Phase Control manages power delivery to your CPU. Set it to “Extreme” for maximum stability or let ASUS boards disable phases at low load to save energy—perfect balance!
Let’s break it down in a way that feels less like a lecture and more like a chat over coffee. By the end, you’ll get what CPU Power Phase Control does and why it’s a big deal for your next build.
What Is CPU Power Phase Control, Anyway?
Imagine your CPU as the brain of your PC, constantly working to keep everything ticking. Brains need fuel. That fuel is power for your CPU—delivered not straight from your wall outlet but through a clever little system called the Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) on your motherboard. The VRM is like a chef, cooking up the perfect voltage and current your CPU needs to thrive.
Here’s where CPU Power Phase Control steps in. The VRM splits power delivery into “phases”—think of them as lanes on a highway. Each phase has its crew of components: MOSFETs (tiny switches controlling current), inductors (smoothing the flow), and capacitors (storing energy bursts).
The more phases, the more evenly the workload gets shared. It’s like having a team of baristas at a busy coffee shop instead of one person juggling everything—things work better.
Power Phase Control is the manager of this team. It decides how many phases are active, how they operate, and when they kick into high gear.
You’ll often see options in your BIOS like “Standard,” “Optimized,” “Extreme,” or “Manual.” Each tweaks how power flows, balancing efficiency, stability, and performance. Pretty cool, right?
Why Does This Matter in 2025?
So, why are we talking about this now? CPUs have gotten insane lately. Back in 2015, a quad-core chip was plenty for most folks. Fast forward to 2025, and we’ve got monsters like the AMD Ryzen 9 9950X with 16 cores and 32 threads or Intel’s Core i9-15900K pushing crazy clocks and multi-die designs.
These chips aren’t just power-hungry—they’re famished. And they’re fussy, too, demanding clean, steady voltage to avoid crashes or overheating.
That’s where modern VRMs and Power Phase Control come to the rescue. In 2024, brands like ASUS, MSI, and Gigabyte started rolling out motherboards with 16-, 20-, or even 24-phase designs—leaps beyond yesteryear’s 4- or 6-phase setups.
Why the upgrade? Today’s CPUs need it. If you’re overclocking a Ryzen 7 9700X past 5.5 GHz, a flimsy VRM might falter, causing voltage spikes or thermal throttling. But a robust, multi-phase VRM with smart Power Phase Control keeps things rock-solid, letting you push your chip to the limit.
Even if you’re not into overclocking, this stuff matters. Modern CPUs use dynamic boosting—think AMD’s Precision Boost or Intel’s Turbo Boost—to juice up performance on demand.
A good VRM ensures those boosts don’t turn into stutters. Plus, with energy efficiency on everyone’s mind, Power Phase Control helps your system save power when it’s idle, keeping your electric bill in check.
Also Read: Is VR CPU Or GPU Intensive – A Complete Performance Guide!
How Does It Actually Work?
Let’s nerd out a bit—but I’ll keep it simple, promise. When your CPU calls for power, the VRM takes the 12V DC from your power supply and steps it down to something the CPU can handle—usually 1-1.5V, depending on the task.
The catch? CPUs don’t want a constant stream. They’re like a kid at a buffet, grabbing big bites during heavy workloads (gaming, rendering) and nibbling when idle (scrolling X).
A single-phase VRM could manage this, but it’d be like one person carrying a whole Thanksgiving feast—something’s getting dropped.
Multiple phases split the load. Each phase delivers power in tiny pulses, controlled by Pulse Width Modulation (PWM). More phases mean smoother delivery—like overlapping waves instead of choppy splashes.
Power Phase Control runs the show. In “Standard” mode, it might use just a few phases for light tasks to save energy. “Optimized” adjusts dynamically—more phases for heavy lifting, fewer when chilling.
“Extreme” goes all-in, firing every phase for maximum stability—perfect for overclocking. Some boards even let you tweak it manually, though the auto settings are usually plenty smart for most of us.
The Evolution of Power Phases: From Basic to Beastly
If you’ve built PCs over the years, you’ve seen VRMs grow. In the early 2000s, a 4-phase VRM was standard on budget boards—fine for Pentium 4s or Athlon 64s, which weren’t precisely power guzzlers. By 2015, 8-phase designs popped up on enthusiast boards, often with heatsinks or heat pipes for cooling.
In 2024 and 2025, we’re in the era of digital VRMs. Unlike older analog setups, digital PWM controllers adjust power with surgical precision, reacting to CPU demands in microseconds.
Pair that with 16+ phase designs—like on the ASUS ROG Crosshair X870E Hero or MSI MEG Z890 ACE—and you have a VRM that can tame even the wildest chips.
Why the leap? Features like AMD’s 3D V-Cache or Intel’s hybrid cores make power delivery trickier, and a top-tier VRM with innovative Power Phase Control keeps every core fed.
Real-World Benefits: What’s In It for You?
Okay, you probably think, “Nice tech talk, but how does this help me?” Great question! Here’s how it shakes out depending on your PC life:
1. Gamers
Are you chasing high FPS in Cyberpunk 2077 or Starfield at 4K? Your CPU’s boosting hard. A solid VRM with good Power Phase Control keeps those boosts steady—no FPS drops or crashes. Budget boards with weak VRMs might struggle with next-gen chips.
2. Content Creators
Rendering 3D animations or editing substantial video files? Multi-core CPUs love consistent power. More phases mean less heat and better longevity—your rig won’t croak after an all-night render.
3. Overclockers
This is your turf. Pushing a Ryzen 5 9600X to 5.8 GHz or an i7-15700K past 6 GHz demands a VRM that can handle extra voltage and heat. “Extreme” settings and a 16+ phase design are your secret weapons.
4. Everyday Users
Are you just browsing or streaming? A well-tuned VRM saves power at idle—lower bills and quieter fans. Less heat means a happier, longer-lasting system.
The Future of Power Phase Control
What’s next for this tech? As CPUs evolve—think 128-core giants or AI-powered chips—VRMs will keep pace. In 2025, we’re seeing hints of liquid-cooled VRMs and integrated power monitoring in software.
Power Phase Control might even get AI-smarts, predicting your workload (gaming at night, editing by day) and tweaking phases on the fly. Imagine a motherboard that learns your habits and optimizes itself—wild, right?
Must Read: CPU DXE Initialization Is Started – Fixing Errors In 2025!
CPU Power Phase Control Extreme
Setting CPU Power Phase Control to “Extreme” means all power lanes to your CPU stay wide open, full blast, all the time! It’s great for stability if you’re overclocking hard, but it uses more power and makes things hotter. Perfect for pushing limits, though!
VDDCR CPU Power Phase Control Optimized or Extreme
So, VDDCR CPU Power Phase Control tweaks how power hits your CPU. “Optimized” saves energy by adjusting lanes based on need—super chill for everyday use. “Extreme” keeps them all on max, which rocks for overclocking but heats up more. It’s your call, depending on your vibe!
CPU Power Thermal Control Asus
With ASUS’s CPU Power Thermal Control, you set a temp limit for your CPU’s power system. It’s like telling your rig, “Hey, don’t get too hot!” You pick a safe number that keeps things cool under pressure—great for extended gaming or heavy tasks.
AI Suite 3 CPU Power Phase Control
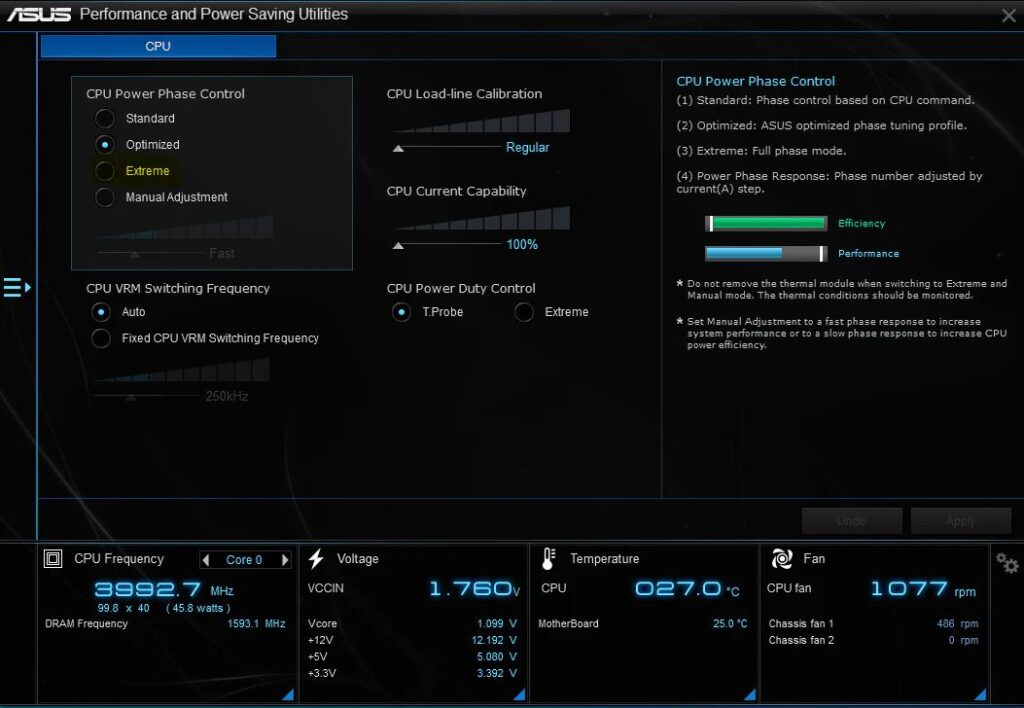
AI Suite 3 lets you tweak how power flows to your CPU! It’s super easy—adjust settings for better speed or less heat. Perfect for keeping your system smooth and stable, whatever you’re up to!
CPU Power Duty Control T Probe or Extreme
CPU Power Duty Control decides how power splits across phases. “T Probe” balances heat, keeping things even and chill—nice for steady use. “Extreme” maxes out current, pushing power hard for significant performance boosts. It’s a trade-off: calm or crazy, your choice!
CPU VRM Thermal Control
CPU VRM Thermal Control watches the heat on your motherboard’s power bits. It’s like a babysitter for the Voltage Regulator Module, ensuring it doesn’t overheat when your CPU works hard. It keeps your system safe and happy, especially during intense moments!
CPU Load Line Calibration
CPU Load Line Calibration stops voltage drops when your CPU gets busy. It’s like propping up a sagging bridge—higher settings keep the power steady for overclocking but use more juice. Lower ones save energy. Pick what fits your style, from chill to wild!
CPU Phase Control On/Off? When Overclocking
Turning the CPU phase control “on” when overclocking keeps power steady—great for pushing limits! “Off” might save energy but could wobble under stress. I’d keep it on for a happier, faster CPU without hiccups!
Read More: Is 60 Degrees Celsius Hot For A CPU: (Safe Temps Explained!)
CPU Power Phase Control in ASUS Z77
On an ASUS Z77, CPU Power Phase Control balances power to your CPU. It’s like giving it just the right juice—set it low for chill tasks or high for gaming. It keeps things cool and steady!
Rampage IV Formula CPU Power Phase Control
The Rampage IV Formula’s Power Phase Control is awesome for tuning your CPU. Crank it up for overclocking power, or dial it back for quiet days. It’s all about keeping your rig happy and strong!
CPU Power Phase Control: Standard or Extreme Mode?
Standard mode saves power and keeps things calm—good for everyday stuff. Extreme mode pumps max power for big tasks or overclocking, but it gets hot! Pick what vibes with your needs!
VRM Switching Frequency & Power Phase Control – Optimal Setting
VRM switching frequency and phase control? Higher settings mean snappy power for gaming—around 500kHz is solid. Pair it with “optimized” phases for daily use. It keeps your CPU fed without overheating—nice and balanced!
FAQs
1. Should CPU Phase Control Be On or Off?
Keep CPU phase control on for steady power—great for gaming! Off saves energy but might stutter when pushing hard. I’d say on!
2. What Is the CPU Power Phase?
It’s how your motherboard splits power to the CPU—like lanes on the road: more lanes, smoother power. Keep your CPU happy and fast!
3. What Is ASUS CPU Power Phase Control?
ASUS’s CPU Power Phase Control tweaks how power hits your CPU. It’s like a dial—turn it up for speed, down for chill vibes!
4. How to Control CPU Power?
Use your BIOS or software like AI Suite to tweak CPU power. Adjust phases or settings—an easy way to balance speed and coolness!
5. What Is the Function of the Phase Control?
Phase control manages power lanes to your CPU. It keeps things steady—less heat, more oomph. Super handy for gaming or big tasks!
6. Does Motherboard Power Phase Matter?
Yep, power phases matter! More phases mean stabler power for your CPU—great for overclocking or heavy use. Cheap boards might struggle, though!
7. Should I Have CPU C States On or Off?
C states on saves power when idle—good for laptops or quiet PCs. Off keeps it full blast for max speed. I’d leave it on!
8. What Is Phase Control?
Phase control splits CPU power into lanes. It’s like teamwork—more lanes, smoother delivery. Keep your system chill and ready for action!
9. Should CPU Frequency Scaling Be On or Off?
On lets your CPU slow down when resting—and saves power. Off locks it fast—better for heavy stuff. I’d keep it on for balance!
10. Should CPU Usage Be High or Low?
High usage is acceptable for big tasks—it means it’s working hard! Low is better for light stuff. Depends on what you’re doing!
Conclusion
So, CPU Power Phase Control keeps your PC’s heart pumping smoothly! Whether gaming or chilling, it balances power, stability, and efficiency. With 2025’s crazy CPUs, it’s a must-know for any build. Tweak it your way—your rig will thank you with excellent performance and a longer life!