When you turn on your computer, a lot happens before you see the startup screen. One of the most critical steps is pre-memory CPU initialization.
Pre Memory CPU Initialization Is Started means the CPU is setting up before accessing memory. This step ensures proper hardware communication, enabling a smooth boot process. Issues here can cause startup errors, requiring BIOS updates or hardware checks.
In this guide, we’ll explain it in simple terms so you can understand it easily. Let’s dive in!
Understanding Pre-Memory CPU Initialization
Pre-memory CPU Initialization refers to the phase in the boot process where the CPU and essential chipset components are initialized before the system’s main memory is made available.
This stage is crucial because, without proper CPU initialization, the system cannot proceed to initialize memory or other hardware components.
During this phase, the system performs several key tasks:
- CPU Microcode Loading: The system updates the CPU’s microcode to ensure it operates correctly and can handle the latest instructions and features.
- Cache Initialization: The CPU’s internal caches are set up to function as temporary storage, which is essential for performance during the early boot stages.
- Basic Chipset Configuration: Essential chipset components, such as the System Agent (responsible for managing communication between the CPU, memory, and PCIe devices), are initialized to prepare for further hardware initialization.
- Temporary Memory Setup: Since the main system memory isn’t yet initialized, the system may set up a temporary memory space using CPU caches (a technique known as “Cache-as-RAM”) to facilitate the boot process.
The Importance of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
Pre-memory CPU initialization is a crucial step in starting your computer. It sets up the CPU before the memory is fully active, ensuring smooth communication between components. Without it, your computer might crash, freeze, or fail to start.
This process configures necessary settings like cache, memory controller, and security features. It also checks for hardware errors early, preventing more significant issues later.
In short, pre-memory CPU initialization is like warming up before a workout—it prepares your system to perform at its best.
1. Overview of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
A. Cache Configuration
Cache is a small, super-fast memory inside the CPU that stores frequently used data. The CPU configures this cache during pre-memory initialization to improve speed and efficiency.
It determines how the cache stores and retrieves data, ensuring the CPU doesn’t waste time looking for information in slower memory.
A well-configured cache reduces delays and makes your computer feel faster. Think of it like organizing a toolbox—when everything is in the right place, you can work more efficiently.
B. Memory Controller Initialization
The memory controller helps the CPU talk to the computer’s RAM. During pre-memory initialization, it gets configured to ensure smooth data transfer.
This step sets the memory speed, timings, and compatibility settings. If done incorrectly, the system could experience crashes, slowdowns, or memory errors.
Imagine a librarian organizing books before a library opens—if everything is sorted correctly, finding and using information becomes much faster and easier. That’s exactly what the memory controller does for your computer.
C. System Management Mode (SMM) Initialization
System Management Mode (SMM) is a unique, hidden mode in your CPU that handles critical tasks like power management and system security.
During pre-memory initialization, SMM is set up to manage low-level functions safely and efficiently. It helps protect the system from failures and ensures smooth hardware operation.
Think of it as a backstage crew in a theater—they ensure everything runs smoothly behind the scenes so that the main show (your operating system) works without problems.
2. CPU Features and Capabilities Initialization
Modern CPUs have advanced features like power-saving modes, virtualization, and security enhancements.
During pre-memory initialization, the system detects and configures these features for the best performance. It ensures your CPU runs efficiently and can fully exploit its capabilities.
Imagine buying a high-tech gadget—you must set it up correctly to use all its features. The CPU won’t work as efficiently without proper initialization, leading to slow performance or limited functionality.
A. Virtualization Support Initialization
Virtualization lets you run multiple operating systems on one computer, like having a Windows and Linux system running side by side.
Pre-memory CPU initialization enables virtualization features, ensuring they work correctly. This is important for businesses, developers, and gamers who use virtual machines.
Think of it like setting up a guest room—if it’s well-prepared, visitors (virtual machines) can stay and function smoothly without interfering with the rest of the house (your central system).
B. Power Management Features Initialization
Power management settings help balance performance and energy use. During pre-memory CPU initialization, the system configures power-saving features like sleep modes and dynamic frequency scaling.
This allows laptops to conserve battery and desktops to reduce electricity consumption. Think of it as a car with an eco-mode—when you don’t need full power, the system slows down to save energy.
Proper power management ensures your computer runs efficiently without overheating or wasting electricity.
C. Performance Settings Initialization
Performance settings determine how fast and efficiently your CPU runs. During pre-memory initialization, settings like turbo boost and overclocking are configured.
This ensures the CPU delivers the best speed when needed while avoiding overheating or instability. It’s like tuning a sports car—if done right, you get maximum speed without damaging the engine.
Properly initialized performance settings ensure your system runs fast and stable, whether gaming, editing videos, or browsing the web.
D. Security Features Initialization
Security is crucial in modern computing. During pre-memory CPU initialization, security features like Trusted Execution Technology and encryption support are activated.
These settings help protect your system from malware, unauthorized access, and cyber threats. It’s like setting up a home security system before moving in—locking doors, installing cameras, and ensuring only trusted people can enter.
Without proper security initialization, your system could be vulnerable to attacks, risking your data and privacy.
3. The Significance of Pre-memory CPU Initialization
Pre-memory CPU initialization is the foundation of a stable and efficient computer system. It prepares the CPU, configures hardware settings, and ensures a smooth boot process. Without it, your computer may not start, run slowly, or experience errors.
Think of it as stretching before a workout—if you skip it, your performance suffers, and problems may arise. A well-executed pre-memory initialization ensures that your system runs at peak performance with stability, security, and efficiency.
Common Issues During Pre-Memory CPU Initialization
While pre-memory CPU initialization is designed to be a seamless process, several issues can arise, hindering the boot process:
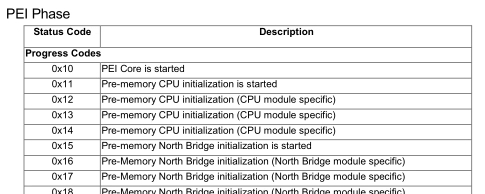
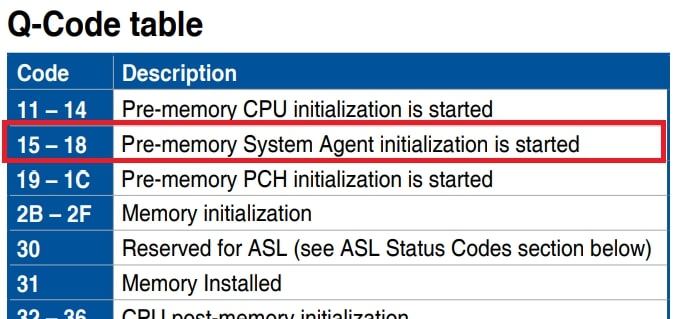
- Error Codes and POST Codes: Many motherboards are equipped with diagnostic LEDs or displays that show POST codes. Codes “15” or “13” often indicate issues during the pre-memory initialization phase. For instance, a user reported encountering error code 15, corresponding to “Pre-memory System Agent initialization is started,” causing the system to hang at this stage.
- Hardware Compatibility Issues: Incompatibilities between the CPU and motherboard or issues with other hardware components can prevent successful pre-memory initialization. For example, unsupported memory modules or incorrect CPU models can lead to initialization failures.
- Firmware Corruption or Misconfiguration: Corrupted or misconfigured BIOS/UEFI firmware can disrupt the initialization process. Incorrect settings, such as improper voltage configurations or disabled essential features, can lead to boot failures.
- Physical Hardware Problems: Physical issues, such as bent CPU pins, improperly seated components, or failing hardware (e.g., a malfunctioning motherboard), can impede the initialization process.
Pre-memory CPU Initialization Process
The pre-memory CPU initialization happens before the system’s RAM is fully active. It starts with basic hardware checks, ensuring the CPU, motherboard, and essential components are working.
Then, it sets up the cache, power settings, and security features. The memory controller is also prepared to handle data efficiently.
This step is like a warm-up routine before a race—ensuring everything is ready for smooth and fast performance. Without it, the system could fail to boot correctly.
Pre-memory CPU Initialization Is Started Q Code
The Q Code during pre-memory CPU initialization helps diagnose boot issues. If the system has trouble starting, it shows specific error codes.
Check the manual to understand the issue if your motherboard displays a Q Code. This helps identify hardware or BIOS-related problems before the system fully boots.
15 Motherboard Code
A motherboard showing Q Code 15 usually means a memory issue. It might be due to incompatible RAM, incorrect installation, or BIOS settings.
To fix it, try reseating the RAM sticks, updating the BIOS, or checking the motherboard manual for troubleshooting steps specific to your system.
Q-Code 14
Q-Code 14 on a motherboard usually means an issue with memory initialization. It could be due to faulty or improperly installed RAM.
To fix it, try reseating the RAM, testing different slots, or updating the BIOS. If the issue continues, check the motherboard manual for specific troubleshooting steps.
Error 15: Pre-Memory Northbridge Initialization
Error 15 happens when the Northbridge (which connects the CPU and memory) isn’t initializing correctly. Incompatible RAM, a BIOS issue, or a faulty CPU can cause this.
Try resetting the BIOS, checking RAM compatibility, or reinstalling the CPU to see if it resolves the problem.
Q Code 15 (Pre-memory System Agent Initialization Is Started)
Q Code 15 means the system agent (which manages CPU communication with memory) is starting but may have issues.
If the system is stuck here, check your RAM, update the BIOS, and ensure all components are seated correctly. A faulty CPU or motherboard could also cause this error.
Q-Code 12, 54, 55 on Asus Z690-E
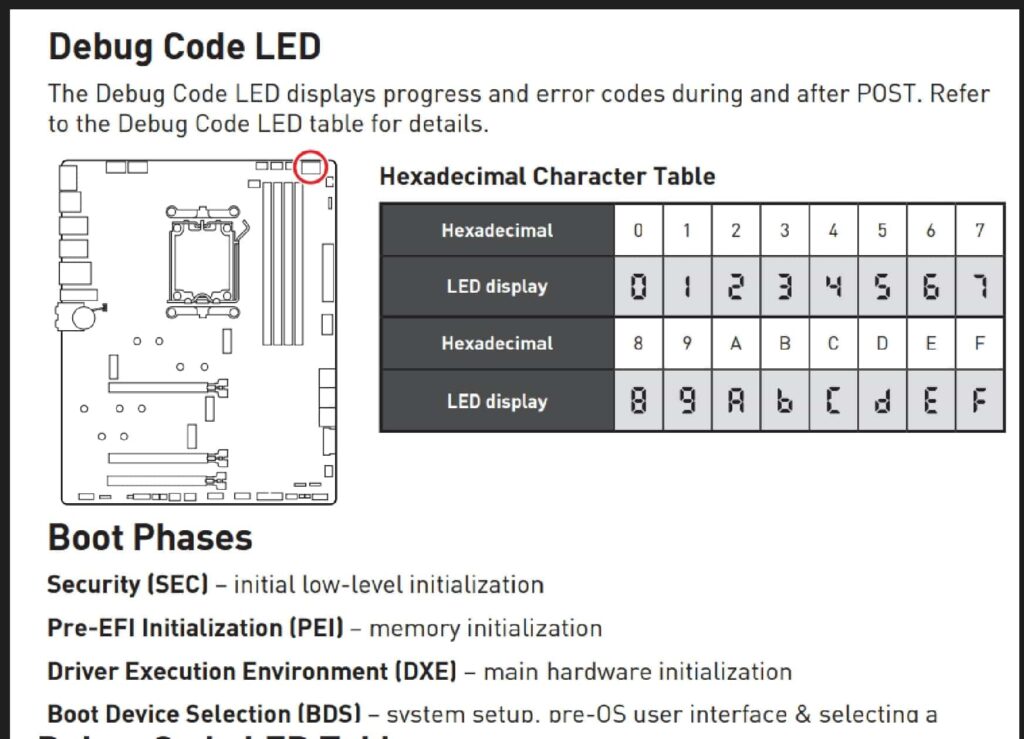
These Q-Codes on an Asus Z690-E motherboard are related to memory issues. Code 12 means CPU initialization, and 54 and 55 indicate RAM problems.
Try reseating the RAM, using different slots, or testing with one stick at a time. Updating the BIOS and checking RAM compatibility can also help.
Motherboard Stuck on CPU Initialization Screen
If your motherboard is stuck on the CPU initialization screen, the system detects the processor incorrectly. Check if the CPU is correctly installed, update the BIOS, and ensure no bent pins on the socket. Testing with a different CPU or motherboard might be necessary if the issue persists.
Fixed! – First Post – ASUS Crosshair VIII Q-code Stops at 15
If your ASUS Crosshair VIII motherboard stops at Q-Code 15, it’s likely a RAM or BIOS issue. Reset the BIOS, try different RAM slots, or update firmware.
Some users fixed it by reseating components or using a single RAM stick first before adding more. Proper troubleshooting can resolve it.
Error Code 15 Pre-memory System Agent Initialization Is Started?
Error Code 15 means the system agent is trying to initialize but isn’t completing the process. This is often due to faulty RAM, an outdated BIOS, or CPU-related issues.
Try reseating RAM, updating the BIOS, and ensuring all components are correctly connected. If the problem continues, check the motherboard manual.
FAQs
1. What does pre-memory CPU initialization is started mean?
This means that the CPU is set up before accessing memory. This step ensures the CPU and motherboard communicate correctly for a smooth system boot.
2. What does CPU post memory initialization mean?
This means the CPU has successfully initialized memory and is now preparing to load the operating system. It’s an essential step in the boot process.
3. What does 15 mean on a motherboard?
Code 15 usually indicates a memory-related issue. It could mean the RAM isn’t detected properly. To fix it, try reseating or replacing your RAM sticks.
4. What is CPU code 00?
Code 00 usually means the CPU isn’t responding. This could be due to incorrect installation, a BIOS issue, or a faulty processor or motherboard.
5. Can RAM cause random restarts?
Yes, faulty or incompatible RAM can cause sudden restarts. If this happens, check your RAM sticks, run a memory test, or try different slots.
6. What is the meaning of memory initialization?
Memory initialization is when the system prepares RAM for use during boot-up. It checks, configures, and ensures memory is ready for the operating system.
7. What happens when a CPU starts?
When a CPU starts, it runs basic checks, initializes memory, and loads the BIOS. Then, it prepares to boot the operating system for full system operation.
8. What is the CPU out of memory error?
This error means the CPU lacks enough available memory for tasks. It can happen due to low RAM, memory leaks, or running too many programs.
9. What is CPU register memory?
CPU register memory is a small, super-fast storage inside the processor. It holds temporary data and instructions to speed up processing and improve performance.
10. Can pre-memory CPU initialization be skipped?
No, pre-memory CPU initialization is necessary. It ensures the CPU and memory communicate correctly. Skipping it could cause boot failures and system instability.
Conclusion
Pre-memory CPU initialization ensures your computer starts correctly and runs smoothly. It prepares the CPU, memory, and other key components for operation, preventing crashes and performance issues. If your system encounters errors during this phase, simple troubleshooting steps like reseating RAM, updating the BIOS, or checking hardware connections can help. Understanding this process enables you to diagnose and fix startup problems efficiently. With the proper knowledge, you can keep your system stable, secure, and performing at its best!