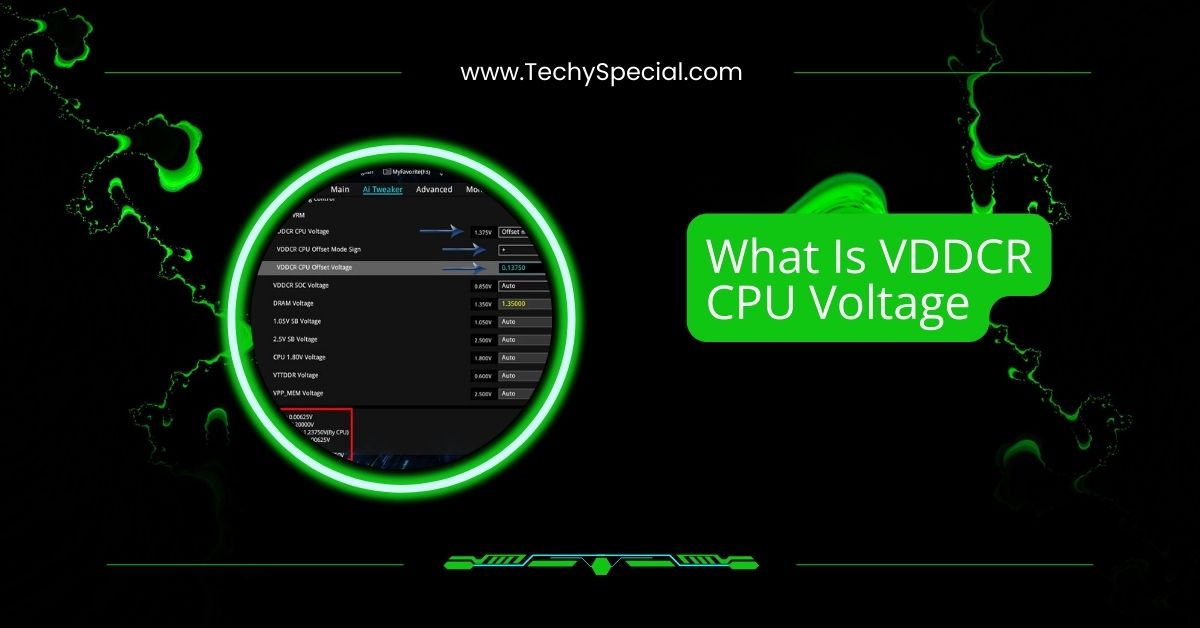
VDDCR CPU Voltage is the power supplied to your processor, helping it run smoothly and efficiently. It plays a key role in performance, stability, and temperature management.
VDDCR CPU Voltage is the power supplied to the processor, typically ranging from 1.350 to 1.375 volts. It helps maintain performance and stability, while VDDCR SOC controls external graphics card memory controllers and other system components.
In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about VDDCR CPU Voltage in simple terms so you can optimize your system with confidence.
Understanding Vddcr CPU Voltage
VDDCR CPU Voltage is the power sent to your processor to keep it running smoothly. It plays a significant role in performance, stability, and heat management.
If the voltage is too high, the CPU gets hot and may wear out faster. If it’s too low, the system might crash or slow down.
Most motherboards adjust it automatically, but advanced users tweak it for better speed or efficiency. Understanding this voltage helps you get the best performance from your PC.
1. Factors Influencing Vddcr CPU Voltage
- CPU Workload – Higher workloads require more power to maintain performance.
- Overclocking – Increasing CPU speed often requires raising the voltage for stability.
- Motherboard Quality – High-end motherboards provide better voltage regulation and stability.
- Cooling System – Good cooling helps manage higher voltages safely and prevents overheating.
- Silicon Lottery – Each CPU is slightly different, meaning some need more voltage than others.
- BIOS Settings – Manual adjustments in BIOS can fine-tune voltage for performance or efficiency.
2. Monitoring and Adjusting Vddcr CPU Voltage
You can monitor your CPU voltage using software like HWMonitor or through your BIOS settings. If your CPU is running too hot or unstable, adjusting the voltage can help.
Lowering voltage reduces heat but may affect performance. Increasing it can boost speed but generate more heat.
BIOS settings allow manual control for experienced users, while automatic modes keep things simple. Regular monitoring ensures your CPU stays within safe limits and performs at its best.
3. The Importance of Vddcr CPU Voltage
VDDCR CPU Voltage is essential for a computer’s performance and lifespan. Too much voltage can overheat and damage your CPU, while too little can cause crashes or slowdowns.
Proper voltage settings help balance power, speed, and temperature, keeping your system stable. Gamers, content creators, and overclockers benefit from fine-tuning it for the best results.
Whether you’re a casual user or an enthusiast, managing CPU voltage properly helps your PC run efficiently and last longer.
The Basics.
1. What is a VRM?
A Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) supplies the correct voltage to your CPU. It ensures stable power, prevents damage, and helps with performance, especially during overclocking. A good VRM improves system efficiency and keeps temperatures lower.
2. What are save voltages for Ryzen APU internal GPU?
For Ryzen APUs, a safe internal GPU voltage is usually between 1.1V and 1.2V. Going higher may improve performance but can cause overheating. When adjusting voltages, always monitor temperatures and stability.
3. What are save voltages for Ryzen SoC?
For safety, the Ryzen SoC voltage should stay between 0.9V and 1.2V. Higher values can increase power consumption and heat. Keeping it within limits ensures stable performance for memory and integrated components.
4. What are save voltages for Ryzen CPU’s?
For Ryzen CPUs, a safe core voltage is typically 1.2V to 1.35V. Over 1.4V can reduce CPU lifespan. Stay below 1.45V with good cooling for overclocking to avoid overheating and instability.
Read Out: CPU Maximum Frequency Always 100: Complete Guide In 2025
BIOS Settings.
1. What is VDDCR CPU Load Line Calibration?
Load Line Calibration (LLC) stabilizes CPU voltage under heavy loads. It prevents voltage drops, improving system stability and overclocking. Higher LLC settings reduce fluctuations but may increase heat and power usage.
2. What is VDDCR CPU Current Capability?
This setting controls how much current the CPU can draw. Increasing it allows higher performance but can cause overheating. Keeping it balanced ensures stable power delivery without damaging components.
3. What is VDDCR CPU Switching Frequency?
Switching frequency determines how often power is regulated to the CPU. Higher values improve power stability but increase heat. Lower values save energy but may reduce overclocking potential.
4. What is VDDCR CPU Power Duty Control?
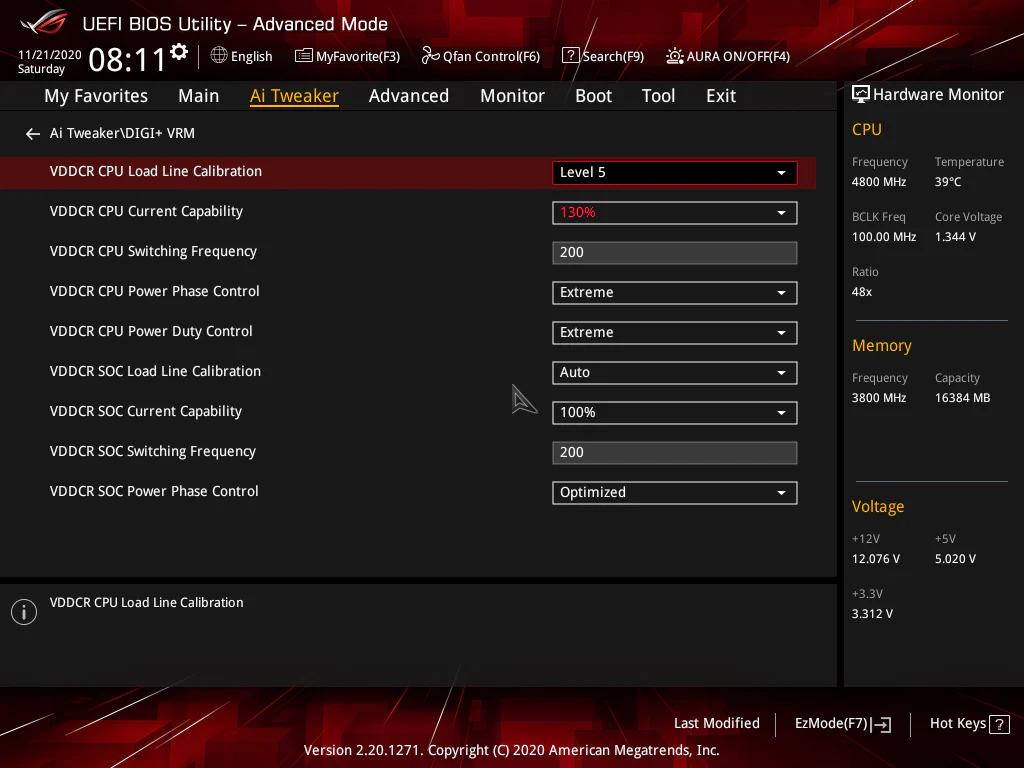
This setting balances power delivery between CPU cores. “T.Probe” distributes power evenly for stability, while “Extreme” focuses power on active cores, improving performance but increasing heat.
5. What is VDDCR CPU Power Phase Control?
Power Phase Control manages how power is distributed to the CPU. “Standard” balances efficiency, while “Extreme” increases power for better performance. It is useful in overclocking but generates more heat.
6. What is SOC?
The SOC (System on Chip) handles CPU communication with memory, PCIe, and integrated graphics. Adjusting the SOC voltage can improve system stability, especially when overclocking RAM or using Ryzen APUs.
7. What is VDDCR SOC Load Line Calibration?
SOC LLC stabilizes voltage for the system bus and memory controller. Higher settings reduce voltage drops but may increase power consumption. It helps when overclocking RAM or using integrated graphics.
8. What is VDDCR SOC Current Capability?
This setting controls the SOC power limit. Increasing it can enhance RAM and integrated GPU performance but may cause overheating. Keeping it within safe limits prevents system instability.
9. What is VDDCR SOC Switching Frequency?
This defines how often the SOC power is regulated. Higher frequencies improve stability but generate heat, while lower frequencies save energy but might reduce performance.
10. What is VDDCR SOC Power Phase Control?
It manages how power is supplied to the SOC. Higher phase control improves stability for memory and GPU performance but may increase power draw and heat.
11. What is VDDCR SOC Voltage?
VDDCR SOC voltage powers memory and integrated GPU functions. Keeping it between 0.9V and 1.2V ensures stability. Higher values help overclocking but increase heat.
12. What is CPU Core Ratio?
CPU Core Ratio controls clock speed by adjusting the multiplier. Increasing it boosts performance but requires higher voltage and better cooling to avoid overheating.
13. What is the GFX clock frequency?
GFX clock frequency determines the speed of the integrated GPU. A higher frequency improves graphics performance but requires more power and cooling.
14. What is the GFX core voltage?
This voltage controls the power of the integrated GPU. Safe values range from 1.1V to 1.2V. Higher voltage boosts performance but increases heat and power consumption.
15. What is DRAM Voltage?
DRAM voltage powers system memory. Safe values range from 1.2V to 1.35V for DDR4. Overvolting can improve RAM speed but may cause instability and overheating.
16. What is Global C-State Control?
This setting manages CPU power-saving states. Enabling it reduces idle power usage, but disabling it can improve performance at the cost of higher energy consumption.
Safe Voltage Ranges for Popular CPUs
Understanding the safe voltage ranges for your specific CPU model is essential to prevent damage and ensure longevity:
- AMD Ryzen CPUs:
- Stock Voltage: Approximately 1.1V to 1.3V
- Safe Overclocking Voltage: Up to 1.4V
- Risky/High Voltage: Above 1.45V (may degrade CPU lifespan)
- Intel Core CPUs:
- Stock Voltage: Approximately 1.0V to 1.25V
- Safe Overclocking Voltage: Up to 1.35V
- Risky/High Voltage: Above 1.4V (can cause overheating and long-term damage)
These values can vary based on the specific CPU model and manufacturing process. Always consult the manufacturer’s guidelines before making voltage adjustments.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage vs Core Voltage?
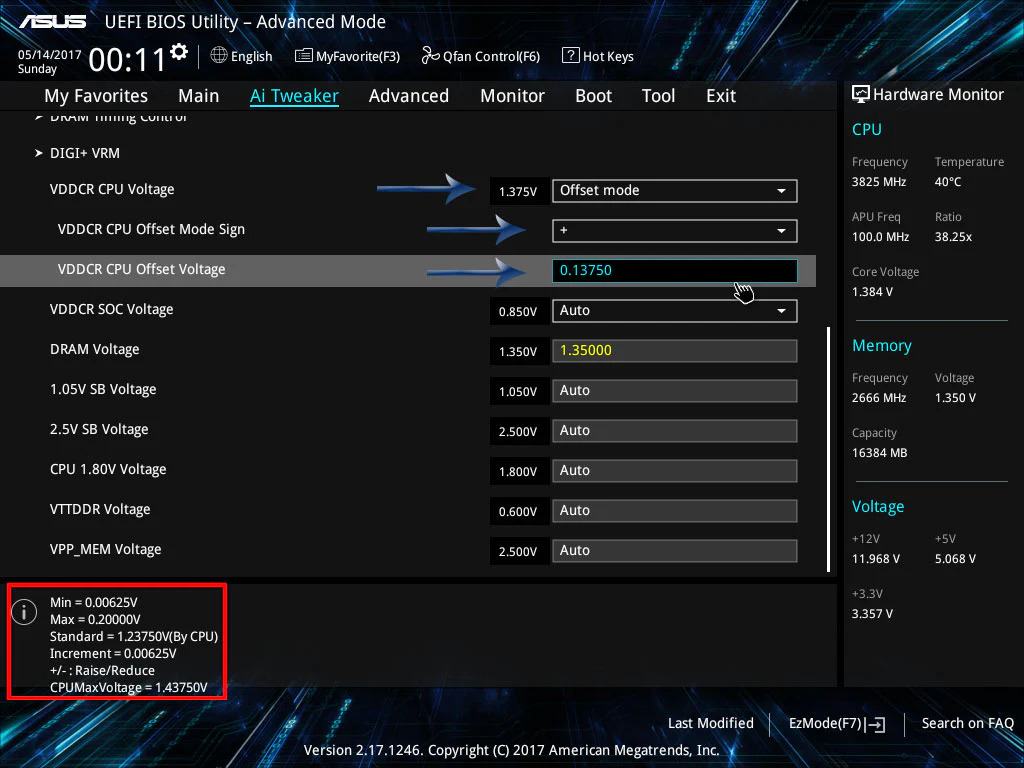
VDDCR CPU Voltage supplies power to the processor, while Core Voltage (Vcore) directly powers CPU cores. VDDCR CPU Voltage affects overall CPU stability, while Vcore influences performance, temperature, and power consumption during high workloads or overclocking.
Must Know: Is 90C Safe For CPU – Causes, Fixes And Prevention Tips!
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Offset Mode?
Offset Mode lets you increase or decrease CPU voltage by a set amount. This helps fine-tune power consumption and temperatures while keeping dynamic voltage adjustments active, ensuring better efficiency and stability without locking the voltage at a fixed level.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Ryzen?
On Ryzen CPUs, VDDCR CPU Voltage powers the processor and affects performance and heat. Safe values range from 1.2V to 1.35V for most setups. Lower voltages improve efficiency, while higher values help with overclocking but increase heat.
What is VDDCR CPU Voltage Ryzen 7?
For Ryzen 7 CPUs, VDDCR CPU Voltage typically ranges from 1.25V to 1.35V under load. Keeping it balanced prevents overheating and ensures stable performance, especially for demanding tasks like gaming, rendering, or overclocking.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Override
Override Mode sets a fixed voltage for the CPU, disabling automatic adjustments. It’s helpful in overclocking but can cause excess heat if set too high. Keeping it within a safe range prevents crashes and extends CPU lifespan.
How to Change VDDCR CPU Voltage?
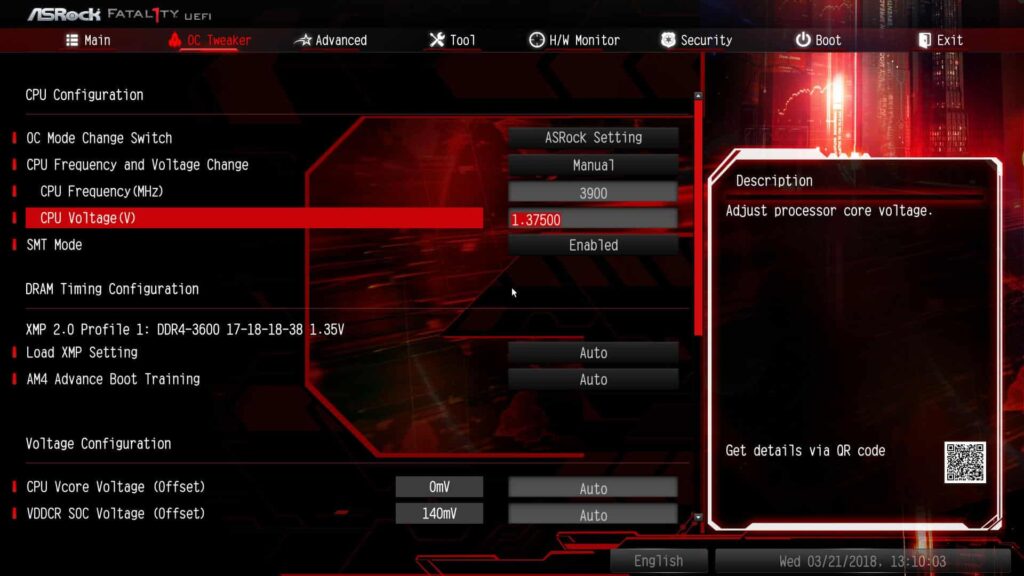
To adjust VDDCR CPU Voltage, enter your BIOS, locate voltage settings under the AI Tweaker or Overclocking tab, and select Offset or Override mode. Increase voltage gradually and monitor temperatures to avoid overheating or system instability.
SoC vs VDDCR SoC?
The SoC (System on Chip) includes the CPU, GPU, and memory controller, while the VDDCR SoC Voltage powers these components.
Proper tuning of the VDDCR SoC ensures stable system performance, especially for Ryzen CPUs with integrated graphics or memory overclocking.
High or Normal VDDCR SoC Voltage?
A normal VDDCR SoC Voltage is around 1.0V to 1.2V. High voltage (above 1.2V) can improve stability for overclocking but may increase heat. Keeping it within safe limits helps maintain performance without stressing the CPU.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Ignored in BIOS (B550-E)?
If BIOS ignores VDDCR CPU Voltage settings, check for BIOS updates, ensure manual voltage control is enabled, and turn off power-saving features like Precision Boost Overdrive (PBO). Some motherboards may override settings based on CPU power limits.
VDDCR CPU Voltage Does Not Match Core Voltage
VDDCR CPU Voltage supplies overall CPU power, while Core Voltage (Vcore) directly powers the CPU cores. Differences occur due to power management features like voltage droop or LLC settings, affecting stability, efficiency, and thermal output.
Ryzen 9 3900X VDDCR CPU and VDDCR SoC Voltage
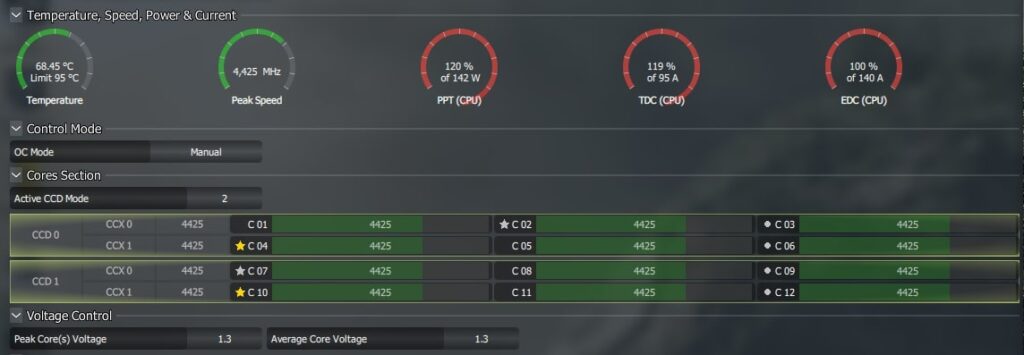
For the Ryzen 9 3900X, the safe VDDCR CPU Voltage is 1.2V to 1.35V, and the safe VDDCR SoC Voltage is around 1.0V to 1.1V. Balancing them ensures optimal performance and stability, especially for high workloads or gaming.
Ryzen 5000: Difference Between VDDCR and Curve Optimizer?
VDDCR controls overall CPU voltage, while Curve Optimizer fine-tunes per-core voltage for better efficiency and performance.
Lowering voltage through Curve Optimizer reduces heat while maintaining boost speeds, helping Ryzen 5000 CPUs run cooler and faster.
FAQs
1. What is a good VDDCR CPU voltage?
For most CPUs, a good VDDCR CPU voltage is 1.2V to 1.35V. Keeping it within this range ensures stability and efficiency.
2. What voltage should CPU be at?
Most CPUs run at 1.0V to 1.4V, depending on load. Lower voltage saves power, while higher voltage supports overclocking but increases heat.
3. What should SOC voltage be set to?
A safe SOC voltage is around 1.0V to 1.2V. Higher values help with memory stability but can increase power consumption.
4. What is VDDCR VDD full mode?
VDDCR VDD Full Mode forces a constant voltage, preventing power fluctuations. This helps overclocking but may increase CPU temperatures.
5. What is a safe CPU voltage?
For most CPUs, 1.2V to 1.35V is safe. Over 1.4V can cause overheating and shorten CPU lifespan, especially without good cooling.
6. What is the VDDCR CPU current capability?
It controls how much current the CPU can draw. Higher values help with overclocking, but if unchecked, they may cause overheating.
7. What is a good voltage for 4.2 GHz?
A stable voltage for 4.2 GHz is 1.2V to 1.35V, depending on the CPU model and cooling efficiency.
8. What is low voltage CPU?
A low-voltage CPU operates at reduced power, usually below 1.0V, improving battery life and efficiency in laptops or energy-saving systems.
Conclusion
VDDCR CPU Voltage is crucial in system stability, performance, and longevity. Properly managing it ensures efficient power usage, prevents overheating, and supports overclocking. Whether you’re a casual user or an enthusiast, understanding CPU voltage helps optimize your system for the best results.